Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0269 - Real-Time Artificial Intelligence in Colonoscopy for Adenoma Detection: A Systematic Review

Ibrahim Mohammed, MD
Albany Medical Center
Waterbury, CT
Presenting Author(s)
1Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY; 2Ain Shams University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt
Introduction:
By offering real-time computer-aided detection systems that alert the endoscopist to suspicious lesions, artificial intelligence (AI) is being utilized increasingly frequently during colonoscopy to improve the detection of polyps. Numerous large randomized controlled trials show that AI-assisted colonoscopy decreases miss rates without increasing procedure duration and dramatically enhances adenoma and polyp detection rates. Our study aimed to evaluate the impact of real-time AI on polyp and adenoma detection during colonoscopy.
Methods:
In May 2025, we searched PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library for studies evaluating real-time AI use during colonoscopy. We included studies that compared AI-assisted colonoscopy with standard or non-AI colonoscopy and reported adenoma detection rate (ADR), polyp detection rate (PDR), or adenoma miss rate (AMR). Two reviewers screened studies and extracted data independently, resolving conflicts by consensus.
Results:
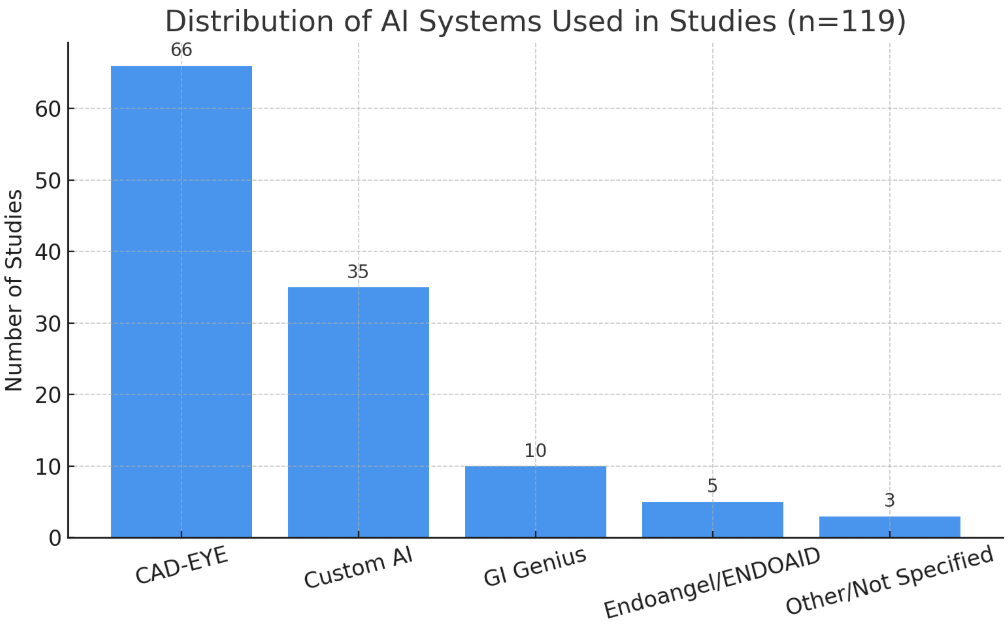
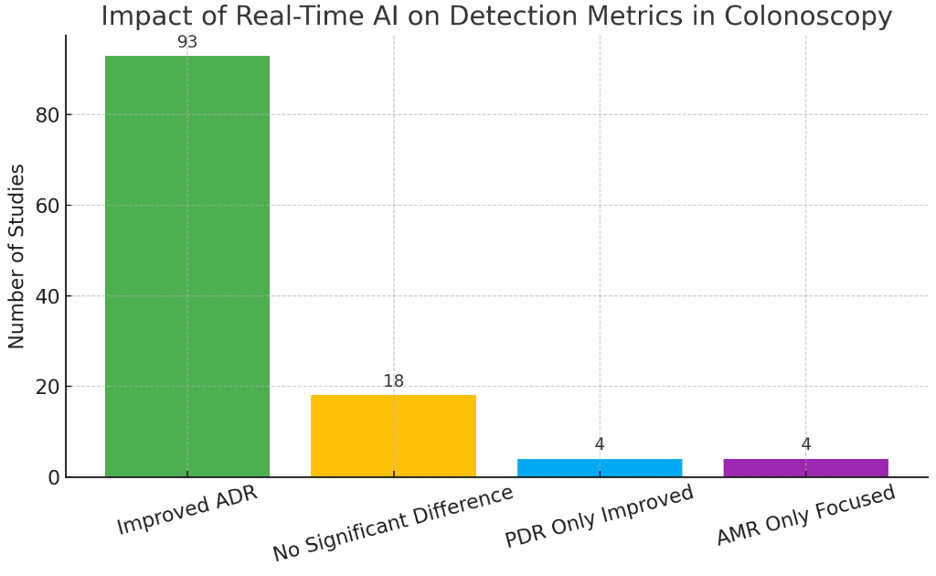
We screened 2,152 studies and included 119 that met our criteria, comprising 72 randomized controlled trials (RCTs), 25 prospective studies, and 19 retrospective studies. All studies involved the real-time application of AI during colonoscopy and compared outcomes with standard or non-AI-assisted colonoscopy. The majority of studies evaluated CAD-EYE (66 studies), followed by custom AI models (35), GI Genius (10), and other systems including Endoangel and Endoaid. Across studies, 93 (78%) demonstrated statistically significant improvement in adenoma detection rate (ADR) with AI, while 18 studies (15%) showed no significant difference. An additional 4 studies reported improvement in polyp detection rate (PDR) without ADR benefit, and 4 studies focused on adenoma miss rate (AMR), all showing reductions in missed lesions with AI assistance. Reported ADRs ranged from 4.5% to 84.97% in AI-assisted groups versus 0.28% to 80% in control groups. Multiple tandem and multicenter trials confirmed that AI can enhance detection even among expert and high-performing endoscopists, with particularly notable gains in lower baseline detection settings. No study reported worse performance with AI.
Discussion:
Across a range of systems, the use of real-time AI during colonoscopy continuously enhanced adenoma detection. These results provide credence to the use of AI to improve quality and lower miss rates. The long-term outcomes should be evaluated in future research.
Disclosures:
Ibrahim Mohammed, MD1, Yehya Maitah, 1, Shamayel Safdar, MBBS1, Zarbakht Nisar, MBBS1, Cade Kelleher, MD1, Osama Alshakhatreh, MD1, Mahima Gill, DO1, Mohammed Mohammed, 2, Seth Richter, MD, FACG1. P0269 - Real-Time Artificial Intelligence in Colonoscopy for Adenoma Detection: A Systematic Review, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
