Sunday Poster Session
Category: Endoscopy Video Forum
P0587 - Contrast-free Endoscopic Ultrasound Imaging of a Vascular Enhancing Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Using Detective Flow Imaging (DFI) With Confirmatory Fine-needle Biopsy
.jpg)
Yingyun (Julie) Yang, MD
Mayo Clinic
Jacksonville, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction:
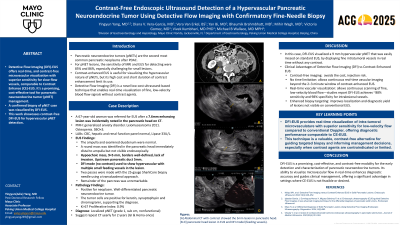
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNETs) are the second most common pancreatic neoplasms and are often hypervascular. Small or iso-echoic lesions may evade detection on conventional imaging. While contrast-enhanced EUS (CE-EUS) improves vascular visualization, its use is limited by cost, short imaging duration, and contraindications. Detective Flow Imaging (DFI) is a novel EUS modality that enables real-time visualization of low-velocity microvascular flow without contrast. Recent studies have shown DFI-EUS to be comparable to CE-EUS in diagnostic accuracy for pancreatic lesions, with sensitivity and specificity reaching 93% and 82%, respectively.
Case Description/Methods:
A 67-year-old woman was referred for EUS after a 5 mm enhancing lesion was incidentally noted in the pancreatic head on CT. Labs were unremarkable. EUS showed a normal ampulla and duodenum. A 9 × 5 mm well-defined, hypoechoic mass was identified distal to the ampulla, not visible endoscopically and easily missed. The remainder of the pancreas was unremarkable and without obvious fatty infiltration. The upstream pancreatic duct was mildly dilated (5 mm), suggesting early obstruction. DFI-EUS revealed rich intralesional vascularity with multiple fine feeding vessels. Two passes were made using a 25G SharkCore needle via a transduodenal approach. Histopathology confirmed a well-differentiated pNET (chromogranin/synaptophysin positive, Ki-67 index 0.9%).
Discussion:
This case highlights the utility of DFI-EUS in detecting and characterizing small pancreatic lesions without contrast. In this case, the decision to biopsy the lesion was due to the fact that it was causing a slight obstruction of the pancreatic duct. DFI-EUS enabled real-time, contrast-free visualization of intratumoral microvasculature, guiding accurate lesion targeting. Compared to conventional Doppler, DFI offers superior sensitivity for slow-flow vessels and continuous high-resolution imaging. Recent literature supports its diagnostic performance as comparable to CE-EUS, particularly in identifying hypervascular lesions such as pNETs and insulinomas. DFI-EUS represents a promising, cost-effective adjunct for early detection and management of pancreatic tumors, especially in patients where contrast use is limited or contraindicated.
Disclosures:
Yingyun Yang, MD, Diana V. Vera-Garcia, MD, Yan Bi, MD, Bhaumik Brahmbhatt, MBBS, MD, Mihir S. Wagh, MD, Victoria Gomez, MD, Vivek Kumbhari, MBChB, PhD, Michael B. Wallace, MD. P0587 - Contrast-free Endoscopic Ultrasound Imaging of a Vascular Enhancing Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Using Detective Flow Imaging (DFI) With Confirmatory Fine-needle Biopsy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

