Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0634 - Systematic Review: Comparison Between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Vonoprazan in Management of Gastric Ulcers, Helicobacter Gastritis, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Post-Procedure Bleeding
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Bipneet Singh, MD
Henry Ford Jackson Hospital
Lexington, KY
Presenting Author(s)
Bipneet Singh, MD1, Rahul Jain, MBBS2, Gurleen Kaur, MBBS3, Palak Grover, MD1, Karanbir Singh, MBBS4
1Henry Ford Jackson Hospital, Jackson, MI; 2Sri Manakula Vinayagar Medical College, Pondicherry, Puducherry, India; 3Government Medical College and Hospital, Khanna, Punjab, India; 4Government Medical College and Hospital, Amritsar, Punjab, India
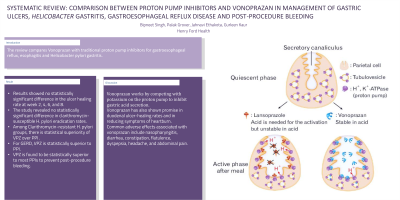
Introduction: Peptic ulcer is defined as a break in the continuity of the epithelial lining the stomach and/ or the duodenum due to active inflammation. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) and NSAIDs are the most common causes of peptic ulcer disease. The review compares Vonoprazan with traditional proton pump inhibitors for gastroesophageal reflux, esophagitis and Helicobacter pylori gastritis.
Methods: The study focused on systematic reviews comparing the use of PPI and Vonoprazan. A literature search was done across PubMed, Google Scholar, Embase, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library. PRISMA guidelines were followed. Cochrane tools were used to measure the risk of bias on multiple fronts. The overall risk was moderate.
Results: Results showed no statistically significant difference in the ulcer healing rate at week 2, 4, 6, and 8. The most effective regimen for treating peptic ulcer disease appears to be lansoprazole 30 mg at both 2 and 8 weeks. At the 4-week mark, pantoprazole 40 mg outperformed vonoprazan 20 mg in terms of efficacy. The study showed that there is no statistically significant difference in clarithromycin-susceptible H. pylori eradication. Among Clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori groups, there is statistical superiority of VPZ over PPI (80% vs 40 %) with a p value of < 0.0001. For GERD, VPZ is statistically superior to Rabeprazole but not with Esomeprazole, lansoprazole, and omeprazole. VPZ is found to be statistically superior to most PPIs to prevent post-procedure bleeding.
Discussion: Vonoprazan is a novel acid inhibitor, which acts by reversible inhibition of potassium competitive acid blocker (P-CAB). It was found to be effective in clarithromycin-resistant Helicobacter pylori and post-procedure bleeding. There was no benefit in gastric ulcer or non-resistant H. pylori.
Disclosures:
Bipneet Singh, MD1, Rahul Jain, MBBS2, Gurleen Kaur, MBBS3, Palak Grover, MD1, Karanbir Singh, MBBS4. P0634 - Systematic Review: Comparison Between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Vonoprazan in Management of Gastric Ulcers, Helicobacter Gastritis, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Post-Procedure Bleeding, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Henry Ford Jackson Hospital, Jackson, MI; 2Sri Manakula Vinayagar Medical College, Pondicherry, Puducherry, India; 3Government Medical College and Hospital, Khanna, Punjab, India; 4Government Medical College and Hospital, Amritsar, Punjab, India
Introduction: Peptic ulcer is defined as a break in the continuity of the epithelial lining the stomach and/ or the duodenum due to active inflammation. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) and NSAIDs are the most common causes of peptic ulcer disease. The review compares Vonoprazan with traditional proton pump inhibitors for gastroesophageal reflux, esophagitis and Helicobacter pylori gastritis.
Methods: The study focused on systematic reviews comparing the use of PPI and Vonoprazan. A literature search was done across PubMed, Google Scholar, Embase, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library. PRISMA guidelines were followed. Cochrane tools were used to measure the risk of bias on multiple fronts. The overall risk was moderate.
Results: Results showed no statistically significant difference in the ulcer healing rate at week 2, 4, 6, and 8. The most effective regimen for treating peptic ulcer disease appears to be lansoprazole 30 mg at both 2 and 8 weeks. At the 4-week mark, pantoprazole 40 mg outperformed vonoprazan 20 mg in terms of efficacy. The study showed that there is no statistically significant difference in clarithromycin-susceptible H. pylori eradication. Among Clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori groups, there is statistical superiority of VPZ over PPI (80% vs 40 %) with a p value of < 0.0001. For GERD, VPZ is statistically superior to Rabeprazole but not with Esomeprazole, lansoprazole, and omeprazole. VPZ is found to be statistically superior to most PPIs to prevent post-procedure bleeding.
Discussion: Vonoprazan is a novel acid inhibitor, which acts by reversible inhibition of potassium competitive acid blocker (P-CAB). It was found to be effective in clarithromycin-resistant Helicobacter pylori and post-procedure bleeding. There was no benefit in gastric ulcer or non-resistant H. pylori.
Disclosures:
Bipneet Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rahul Jain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gurleen Kaur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Palak Grover indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karanbir Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bipneet Singh, MD1, Rahul Jain, MBBS2, Gurleen Kaur, MBBS3, Palak Grover, MD1, Karanbir Singh, MBBS4. P0634 - Systematic Review: Comparison Between Proton Pump Inhibitors and Vonoprazan in Management of Gastric Ulcers, Helicobacter Gastritis, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Post-Procedure Bleeding, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
