Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1147 - Efficacy of Guselkumab in Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis by Extent of Disease and Inflammatory Burden: Subgroup Analysis of the Phase 3 QUASAR Maintenance Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Jessica R. Allegretti, MD, MPH, FACG
Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Jessica R.. Allegretti, MD, MPH1, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD2, Brian Bressler, MD, MS3, Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet, MD, PhD4, Matthew Germinaro, MD5, Shadi Yarandi, MD5, Nicole Shipitofsky, PharmD5, Ye Miao, MS5, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG6, David T. Rubin, MD7, Axel Dignass, MD, PhD8
1Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 3University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada; 4Department of Gastroenterology, CHRU Nancy, INSERM NGERE, Université de Lorraine, France, Vandœuvre-lès-Nancy, Lorraine, France; 5Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA; 6Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, New York, NY; 7University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL, USA, Chicago, IL; 8Agaplesion Markus Hospital, Frankfurt, Hessen, Germany
Introduction: Guselkumab (GUS) is a dual-acting IL-23 inhibitor.1 In the Phase 3 QUASAR maintenance study (NCT04033445), both the GUS 100mg every 8 weeks (q8w) and 200mg q4w subcutaneous (SC) maintenance dose regimens were efficacious.2 Here, we evaluated efficacy of these dose regimens in clinically relevant subgroups of participants (pts) with and without extensive ulcerative colitis (UC) disease or high inflammatory burden.
Methods: Clinical responders after 12 weeks of GUS intravenous (IV) induction were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100mg SC q8w, GUS 200mg SC q4w or placebo (PBO) (GUS withdrawal) at start of the maintenance study (M-0). Efficacy endpoints were analyzed at Week (W)44 in the primary analysis population of pts randomized and treated in the maintenance study who had a modified Mayo score of 5-9 at induction baseline (I-0). Subgroup analyses were conducted by (1) extent of UC disease (limited to left side of colon vs extensive) based on screening endoscopy and/or medical history at I-0 and (2) inflammatory burden based on serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (≤3 vs >3mg/L) at M-0.
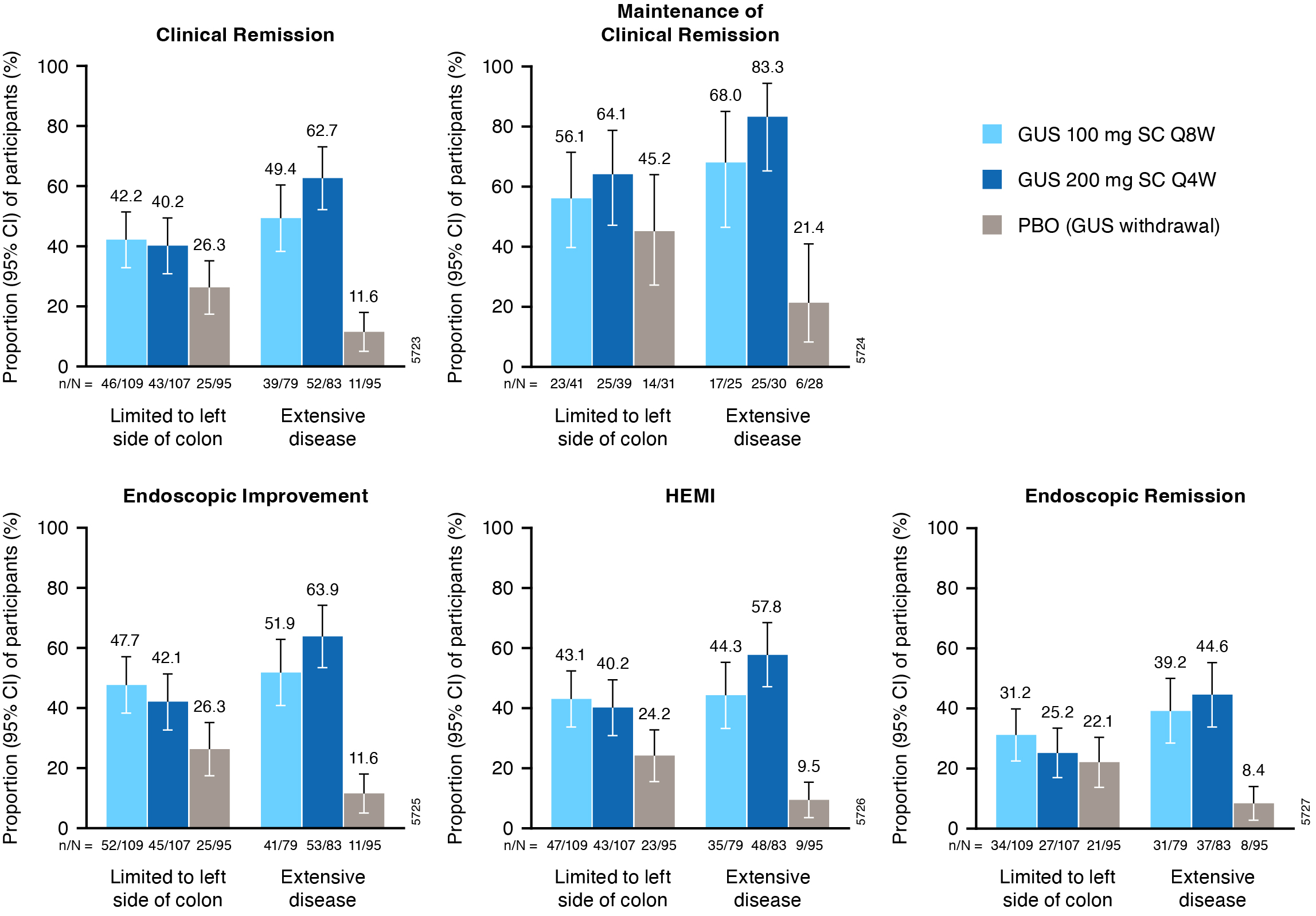
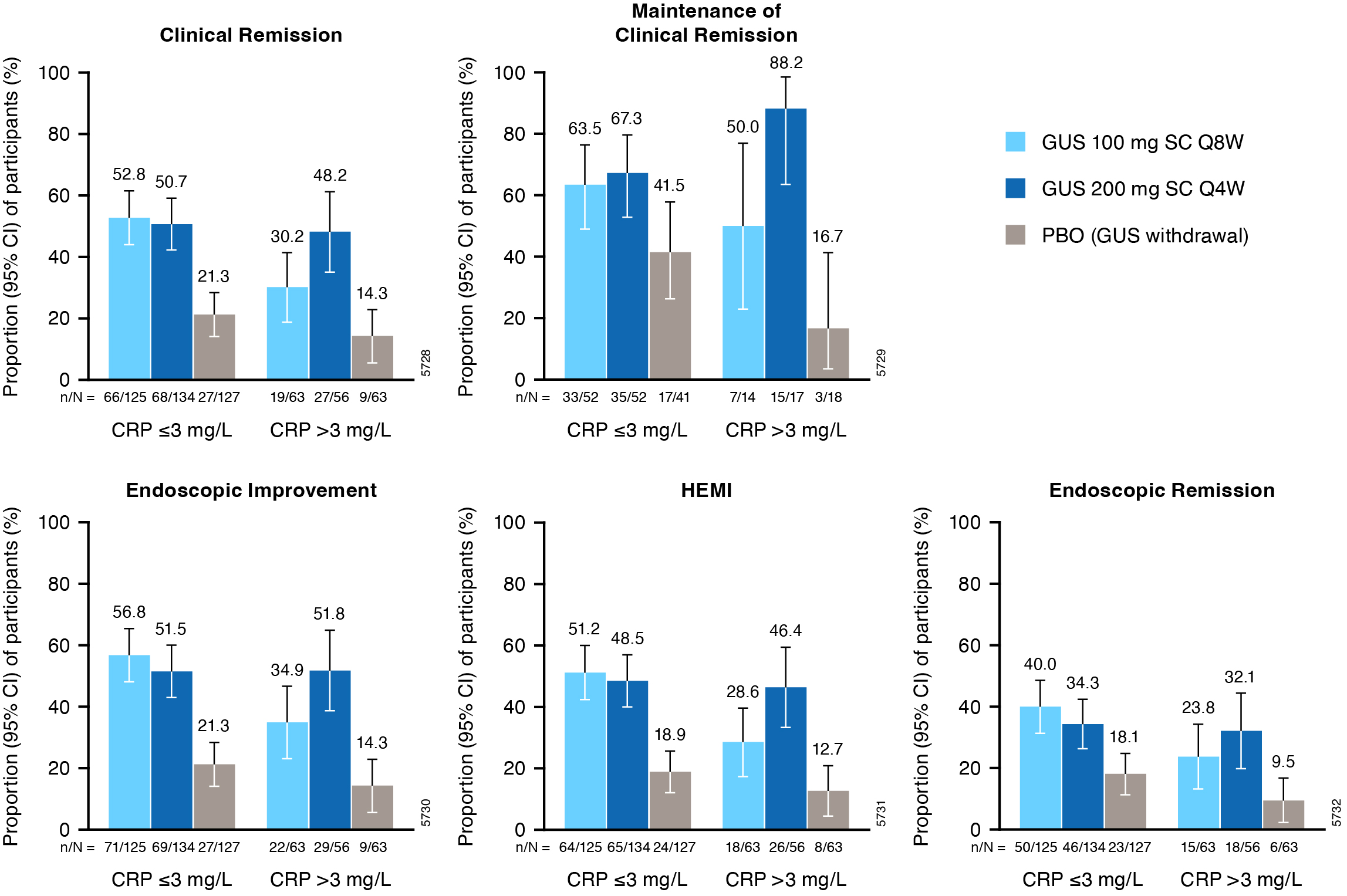
Results: Of 568 pts in the primary analysis population, 257 (45.2%) had extensive UC disease at I-0 and 182 (32.0%) had serum CRP >3mg/L at M-0. Proportions of pts achieving W44 clinical and histologic-endoscopic efficacy endpoints were greater with both GUS dose regimens vs PBO across subgroups (Figures). For pts with extensive UC disease, the proportion of pts achieving clinical remission at W44 was numerically greater with GUS 200mg q4w (62.7%) relative to GUS 100mg q8w (49.4%) (PBO, 11.6%). For those with elevated CRP ( >3mg/L) at M-0, clinical remission at W44 was achieved by 48.2% of GUS 200mg q4w vs 30.2% of GUS 100mg q8w pts (PBO, 14.3%). Proportions of pts achieving endoscopic improvement, histo-endoscopic improvement, endoscopic remission, and maintenance of clinical remission were also greater with GUS 200mg q4w in these subgroups. Among pts with disease limited to the left side of the colon or CRP ≤3mg/L at M-0, proportions of pts achieving these efficacy endpoints were similar with GUS 100mg q8w and GUS 200mg q4w.
Discussion: For pts with moderately to severely active UC with extensive disease or high inflammatory burden, greater efficacy rates were observed with GUS 200mg SC q4w compared with GUS 100mg SC q8w.
References: 1. Sachen KL et al. Front Immunol 2025;16:1532852; 2. Rubin DT et al. Lancet 2025;405:33-49.
Disclosures:
Jessica R.. Allegretti, MD, MPH1, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD2, Brian Bressler, MD, MS3, Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet, MD, PhD4, Matthew Germinaro, MD5, Shadi Yarandi, MD5, Nicole Shipitofsky, PharmD5, Ye Miao, MS5, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG6, David T. Rubin, MD7, Axel Dignass, MD, PhD8. P1147 - Efficacy of Guselkumab in Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis by Extent of Disease and Inflammatory Burden: Subgroup Analysis of the Phase 3 QUASAR Maintenance Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Jessica R.. Allegretti, MD, MPH1, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD2, Brian Bressler, MD, MS3, Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet, MD, PhD4, Matthew Germinaro, MD5, Shadi Yarandi, MD5, Nicole Shipitofsky, PharmD5, Ye Miao, MS5, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG6, David T. Rubin, MD7, Axel Dignass, MD, PhD8
1Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 3University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada; 4Department of Gastroenterology, CHRU Nancy, INSERM NGERE, Université de Lorraine, France, Vandœuvre-lès-Nancy, Lorraine, France; 5Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA; 6Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, New York, NY; 7University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL, USA, Chicago, IL; 8Agaplesion Markus Hospital, Frankfurt, Hessen, Germany
Introduction: Guselkumab (GUS) is a dual-acting IL-23 inhibitor.1 In the Phase 3 QUASAR maintenance study (NCT04033445), both the GUS 100mg every 8 weeks (q8w) and 200mg q4w subcutaneous (SC) maintenance dose regimens were efficacious.2 Here, we evaluated efficacy of these dose regimens in clinically relevant subgroups of participants (pts) with and without extensive ulcerative colitis (UC) disease or high inflammatory burden.
Methods: Clinical responders after 12 weeks of GUS intravenous (IV) induction were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100mg SC q8w, GUS 200mg SC q4w or placebo (PBO) (GUS withdrawal) at start of the maintenance study (M-0). Efficacy endpoints were analyzed at Week (W)44 in the primary analysis population of pts randomized and treated in the maintenance study who had a modified Mayo score of 5-9 at induction baseline (I-0). Subgroup analyses were conducted by (1) extent of UC disease (limited to left side of colon vs extensive) based on screening endoscopy and/or medical history at I-0 and (2) inflammatory burden based on serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (≤3 vs >3mg/L) at M-0.
Results: Of 568 pts in the primary analysis population, 257 (45.2%) had extensive UC disease at I-0 and 182 (32.0%) had serum CRP >3mg/L at M-0. Proportions of pts achieving W44 clinical and histologic-endoscopic efficacy endpoints were greater with both GUS dose regimens vs PBO across subgroups (Figures). For pts with extensive UC disease, the proportion of pts achieving clinical remission at W44 was numerically greater with GUS 200mg q4w (62.7%) relative to GUS 100mg q8w (49.4%) (PBO, 11.6%). For those with elevated CRP ( >3mg/L) at M-0, clinical remission at W44 was achieved by 48.2% of GUS 200mg q4w vs 30.2% of GUS 100mg q8w pts (PBO, 14.3%). Proportions of pts achieving endoscopic improvement, histo-endoscopic improvement, endoscopic remission, and maintenance of clinical remission were also greater with GUS 200mg q4w in these subgroups. Among pts with disease limited to the left side of the colon or CRP ≤3mg/L at M-0, proportions of pts achieving these efficacy endpoints were similar with GUS 100mg q8w and GUS 200mg q4w.
Discussion: For pts with moderately to severely active UC with extensive disease or high inflammatory burden, greater efficacy rates were observed with GUS 200mg SC q4w compared with GUS 100mg SC q8w.
References: 1. Sachen KL et al. Front Immunol 2025;16:1532852; 2. Rubin DT et al. Lancet 2025;405:33-49.

Figure: Figure 1. Key efficacy endpoints at maintenance W44 in subgroups of pts from QUASAR defined by extent of UC disease (limited to left side of colon vs extensive) at induction baseline.
Includes pts with modified Mayo score of 5-9 at induction baseline who achieved clinical response to GUS induction and were re randomized at maintenance study entry.
Error bars represent 95% CIs for proportions of pts meeting the endpoint in each group based on the normal approximation confidence limits, except for maintenance of clinical remission where CIs were based on the exact confidence limits.
Clinical remission is defined as a stool frequency subscore of 0 or 1 and not increased from induction baseline, a rectal bleeding subscore of 0, and an endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 with no friability. Maintenance of clinical remission is defined as clinical remission at W44 among pts in clinical remission at maintenance baseline (denominator is pts with clinical remission at maintenance baseline). Endoscopic improvement is defined as an endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 with no friability. HEMI is defined as achieving a combination of histologic improvement and endoscopic improvement. Endoscopic remission is defined as an endoscopy subscore of 0.
Pts who had an ostomy or colectomy, dose adjustment, prohibited change in UC medication, or who discontinued study agent due to lack of efficacy or an AE of worsening of UC prior to W44 were considered not to have achieved the efficacy endpoints. For pts who discontinued study agent due to COVID-19 related reasons (excluding COVID-19 infection) or regional crisis in Russia and Ukraine prior to W44, the observed values were used if available. Pts who discontinued study agent for other reasons prior to W44 were considered not to have achieved the endpoint. Nonresponder imputation for missing data: pts who were missing one or more of the components pertaining to an endpoint at W44 were considered not to have achieved the endpoint. Pts who had an unevaluable biopsy were considered not to have achieved histologic endpoints.
AE=Adverse event; CI=Confidence interval; GUS=Guselkumab; HEMI=Histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement; PBO=Placebo; pts=Participants; Q4W=Every 4 weeks; Q8W=Every 8 weeks; SC=Subcutaneous; UC=Ulcerative colitis; W=Week.
Includes pts with modified Mayo score of 5-9 at induction baseline who achieved clinical response to GUS induction and were re randomized at maintenance study entry.
Error bars represent 95% CIs for proportions of pts meeting the endpoint in each group based on the normal approximation confidence limits, except for maintenance of clinical remission where CIs were based on the exact confidence limits.
Clinical remission is defined as a stool frequency subscore of 0 or 1 and not increased from induction baseline, a rectal bleeding subscore of 0, and an endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 with no friability. Maintenance of clinical remission is defined as clinical remission at W44 among pts in clinical remission at maintenance baseline (denominator is pts with clinical remission at maintenance baseline). Endoscopic improvement is defined as an endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 with no friability. HEMI is defined as achieving a combination of histologic improvement and endoscopic improvement. Endoscopic remission is defined as an endoscopy subscore of 0.
Pts who had an ostomy or colectomy, dose adjustment, prohibited change in UC medication, or who discontinued study agent due to lack of efficacy or an AE of worsening of UC prior to W44 were considered not to have achieved the efficacy endpoints. For pts who discontinued study agent due to COVID-19 related reasons (excluding COVID-19 infection) or regional crisis in Russia and Ukraine prior to W44, the observed values were used if available. Pts who discontinued study agent for other reasons prior to W44 were considered not to have achieved the endpoint. Nonresponder imputation for missing data: pts who were missing one or more of the components pertaining to an endpoint at W44 were considered not to have achieved the endpoint. Pts who had an unevaluable biopsy were considered not to have achieved histologic endpoints.
AE=Adverse event; CI=Confidence interval; GUS=Guselkumab; HEMI=Histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement; PBO=Placebo; pts=Participants; Q4W=Every 4 weeks; Q8W=Every 8 weeks; SC=Subcutaneous; UC=Ulcerative colitis; W=Week.

Figure: Figure 2. Key efficacy endpoints at maintenance W44 in subgroups of pts defined by inflammatory burden (serum CRP ≤3 vs >3mg/L) at maintenance study baseline.
Includes pts with modified Mayo score of 5-9 at induction baseline who achieved clinical response to GUS induction and were re randomized at maintenance study entry.
Error bars represent 95% CIs for proportions of pts meeting the endpoint in each group based on the normal approximation confidence limits, except for maintenance of clinical remission where CIs were based on the exact confidence limits.
Clinical remission is defined as a stool frequency subscore of 0 or 1 and not increased from induction baseline, a rectal bleeding subscore of 0, and an endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 with no friability. Maintenance of clinical remission is defined as clinical remission at W44 among pts in clinical remission at maintenance baseline (denominator is pts with clinical remission at maintenance baseline). Endoscopic improvement is defined as an endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 with no friability. HEMI is defined as achieving a combination of histologic improvement and endoscopic improvement. Endoscopic remission is defined as an endoscopy subscore of 0.
Pts who had an ostomy or colectomy, dose adjustment, prohibited change in UC medication, or who discontinued study agent due to lack of efficacy or an AE of worsening of UC prior to W44 were considered not to have achieved the efficacy endpoints. For pts who discontinued study agent due to COVID-19 related reasons (excluding COVID-19 infection) or regional crisis in Russia and Ukraine prior to W44, the observed values were used if available. Pts who discontinued study agent for other reasons prior to W44 were considered not to have achieved the endpoint. Nonresponder imputation for missing data: pts who were missing one or more of the components pertaining to an endpoint at W44 were considered not to have achieved the endpoint. Pts who had an unevaluable biopsy were considered not to have achieved histologic endpoints.
AE=Adverse event; CI=Confidence interval; CRP=C-reactive protein; GUS=Guselkumab; HEMI=Histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement; PBO=Placebo; pts=Participants; Q4W=Every 4 weeks; Q8W=Every 8 weeks; SC=Subcutaneous; UC=Ulcerative colitis; W=Week.
Includes pts with modified Mayo score of 5-9 at induction baseline who achieved clinical response to GUS induction and were re randomized at maintenance study entry.
Error bars represent 95% CIs for proportions of pts meeting the endpoint in each group based on the normal approximation confidence limits, except for maintenance of clinical remission where CIs were based on the exact confidence limits.
Clinical remission is defined as a stool frequency subscore of 0 or 1 and not increased from induction baseline, a rectal bleeding subscore of 0, and an endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 with no friability. Maintenance of clinical remission is defined as clinical remission at W44 among pts in clinical remission at maintenance baseline (denominator is pts with clinical remission at maintenance baseline). Endoscopic improvement is defined as an endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 with no friability. HEMI is defined as achieving a combination of histologic improvement and endoscopic improvement. Endoscopic remission is defined as an endoscopy subscore of 0.
Pts who had an ostomy or colectomy, dose adjustment, prohibited change in UC medication, or who discontinued study agent due to lack of efficacy or an AE of worsening of UC prior to W44 were considered not to have achieved the efficacy endpoints. For pts who discontinued study agent due to COVID-19 related reasons (excluding COVID-19 infection) or regional crisis in Russia and Ukraine prior to W44, the observed values were used if available. Pts who discontinued study agent for other reasons prior to W44 were considered not to have achieved the endpoint. Nonresponder imputation for missing data: pts who were missing one or more of the components pertaining to an endpoint at W44 were considered not to have achieved the endpoint. Pts who had an unevaluable biopsy were considered not to have achieved histologic endpoints.
AE=Adverse event; CI=Confidence interval; CRP=C-reactive protein; GUS=Guselkumab; HEMI=Histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement; PBO=Placebo; pts=Participants; Q4W=Every 4 weeks; Q8W=Every 8 weeks; SC=Subcutaneous; UC=Ulcerative colitis; W=Week.
Disclosures:
Jessica Allegretti: Abbvie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker, Speakers Bureau. Adiso – Consultant. Bristol Myer Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Finch – Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Iterative Scopes – Consultant. Janssen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker. Merck – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Roivant – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roivant Adiso – Consultant. Seres Therapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Shattuck Labs – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. TRXBio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Vedanta – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Tadakazu Hisamatsu: AbbVie GK – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Boston Scientific Corporation – Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Honararium. EA Pharma Co. Ltd. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. JIMRO Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. Kissei Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Lilly – Consultant. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Mochida Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Nichi-Iko Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd – Consultant. Nippon Kayaku Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Zeria Pharmaceutical Co – Grant/Research Support.
Brian Bressler: Abbvie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Alimentiv – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Allergan – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Amgen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support. AMT – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Bausch Health – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Celgene – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Eupraxia Fresenius Kabi – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Genentech/Roche – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support. Gilead – Advisor or Review Panel Member. GlaxoSmithKline – Grant/Research Support. Iterative Scopes – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Jamp – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Johnson & Johnson – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Merck – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Microbiome Insights – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Mylan – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Novartis – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Organaon – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Pendopharm – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Pfizer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Protagonist – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Qu Biologic – Grant/Research Support, Stock Options. Sandoz – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Viatris – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet: AbbVie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Abivax – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Adacyte – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Alfasigma – Speakers Bureau. Alimentiv – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Amgen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Applied Molecular Transport – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Arena – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Banook – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Biogen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Connect Biopharm – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. Cytoki Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Eli Lilly – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Enthera – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Fresenius Kabi – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria. Galapagos – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Genentech – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Gilead – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Gossamer Bio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. GSK – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. IAC Image Analysis – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Index Pharmaceuticals – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Inotrem – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Janssen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. Medac – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Mopac – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Morphic – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. MSD – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Nordic Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Novartis – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Oncodesign Precision Medicine – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. ONO Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. OSE Immunotherapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Pandion Therapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Par' Immune – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Pfizer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Prometheus – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Protagonist – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Samsung – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Sandoz – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Sanofi – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Satisfay – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Takeda – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Telavant – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Theravance – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Thermo Fischer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. Tigenix – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Tillots – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Vectivbio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Ventyx – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Viatris – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Ysopia – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria.
Matthew Germinaro: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Shadi Yarandi: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Nicole Shipitofsky: Johnson & Johnson – Employee.
Ye Miao: Johnson & Johnson – Employee.
Bruce Sands: AbbVie – Consultant. Abivax – Consultant, speaking fees. Adiso Therapeutics – Consultant. Agomab Therapeutics – Consultant. Alimentiv – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant. AnaptysBio – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Artugen Therapeutics – Consultant. Astra Zeneca – Consultant. Biolojic Design – Consultant. Biora Therapeutics – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Boston Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Calibr – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Eli Lilly & Company – Consultant, speaking fees. Enthera – Consultant. Enveda Biosciences – Consultant. Equillium – Consultant. Evommune – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Fzatat – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech (Roche) – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant. Gossamer Bio – Consultant. Imhotex – Consultant. Index Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Innovation Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Janssen R&D – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Kaleido – Consultant. Kallyope – Consultant. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA – Consultant. Microba – Consultant. Mobius Care – Consultant. Morphic Therapeutics – Consultant. MRM Health – Consultant. Nexus Therapeutics – Consultant. Nimbus Discovery – Consultant. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Progenity – Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant. Prometheus Laboratories – Consultant. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant. Q32 Bio – Consultant. Rasayana Therapeutics – Consultant. Recludix Therapeutics – Consultant. Reistone Biopharma – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Spyre Therapeutics – Consultant. Sun Pharma – Consultant. Surrozen – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Target RWE – Consultant. Teva – Consultant. Theravance Biopharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. TLL Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Tr1X – Consultant. Union Therapeutics – Consultant. Ventyx Biosciences – Consultant, Stock Options.
David Rubin: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Abivax SA – Consultant. Altrubio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker feees, Stock Options. Avalo – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Bausch Health – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Buhlmann Diagnostics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Connect BioPharma – Consultant. Cornerstones Health, Inc – Board of Directors membership. Douglas Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eli Lilly & Co. – Consultant. Foresee, Genentech (Roche) Inc. – Consultant. Image Analysis Group – Consultant. InDex Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Intouch Group – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Iterative Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Iterative Health – Stock Options. Janssen Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Sanofi – Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker fees. Throne – Consultant. Vedanta – Consultant.
Axel Dignass: Abbvie – Consultant, fees for participation in clinical trials, review activities such as data monitoring boards, statistical analysis and endpoint committees; manuscripts, Speakers Bureau. Abivax – fees for participation in clinical trials, review activities such as data monitoring boards, statistical analysis and end point committees. Amgen – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Biogen – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. CED Service GmbH – Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Dr Falk Foundation – Consultant, fees for participation in clinical trials, review activities such as data monitoring boards, statistical analysis and endpoint committees; manuscripts, Speakers Bureau. Ferring – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant, fees for participation in clinical trials, review activities such as data monitoring boards, statistical analysis and end point committees, Speakers Bureau. Gilead – fees for participation in clinical trials, review activities such as data monitoring boards, statistical analysis and end point committees, Speakers Bureau. High5MD – Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, fees for participation in clinical trials, review activities such as data monitoring boards, statistical analysis and endpoint committees; manuscripts, Speakers Bureau. Lilly – Consultant. Materia – Speakers Bureau. MedToday – Speakers Bureau. MSD – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Consultant, fees for participation in clinical trials, review activities such as data monitoring boards, statistical analysis and end point committees, Speakers Bureau. Pharmacosmos – Consultant. Prima – Speakers Bureau. Roche – Consultant. Sandoz – Consultant. Stada – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, manuscript preparation, Speakers Bureau. Thieme – manuscript preparation. Tilliots – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. UniMed Verlag – manuscript preparation. Vifor Pharma – Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Jessica R.. Allegretti, MD, MPH1, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD2, Brian Bressler, MD, MS3, Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet, MD, PhD4, Matthew Germinaro, MD5, Shadi Yarandi, MD5, Nicole Shipitofsky, PharmD5, Ye Miao, MS5, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG6, David T. Rubin, MD7, Axel Dignass, MD, PhD8. P1147 - Efficacy of Guselkumab in Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis by Extent of Disease and Inflammatory Burden: Subgroup Analysis of the Phase 3 QUASAR Maintenance Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

