Sunday Poster Session
Category: Infections and Microbiome
P1282 - Impact of Protein-Calorie Malnutrition on One-Year Cardiovascular and Thromboembolic Outcomes in Patients With Clostridioides difficile Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Rashid Abdel-Razeq, MD
Cleveland Clinic Foundation
Cleveland, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Rashid Abdel-Razeq, MD1, Chidera Onwuzo, MBBS2, Somtochukwu Onwuzo, MD3, Kojo-Frimpong B. Awuah, MD4, Mohamad-Noor Abu-Hammour, MD5, Barish Eren, MD1, Antoine Boustany, MD6, Lana Dardari, MD7, Basil Jalamneh, MD1
1Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 2SUNY Upstate Medical University Hospital, Syracuse, NY; 3Allegheny Center for Digestive Health, Pittsburgh, PA; 4Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA; 5Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 6Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, FL; 7Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Westlake, OH
Introduction: Malnutrition has significant health implications, contributing to increased morbidity, mortality, and prolonged hospitalizations in patients. Its impact in patients with Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) has not been thoroughly evaluated. In this study, we aim to examine the relationship between PCM and once-year cardiovascular and thromboembolic outcomes in patients with CDI within the United States.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of deidentified, aggregate patient data from TriNetX research network. The cohort compromised patients 18 years of age or older with a diagnosis of CDI. Within this cohort, patients with and without PCM were identified. Primary outcomes were one-year cardiovascular and thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism (PE), deep vein thrombosis (DVT), atrial fibrillation (AF), ventricular fibrillation (VF), ventricular tachycardia (VT), myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure exacerbation, stroke, and cardiac arrest. Variables including age, sex, comorbidities, and other factors known to confound the association between PCM and the composite outcomes underwent 1:1 propensity score matching. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was also utilized to analyze the matched cohorts.
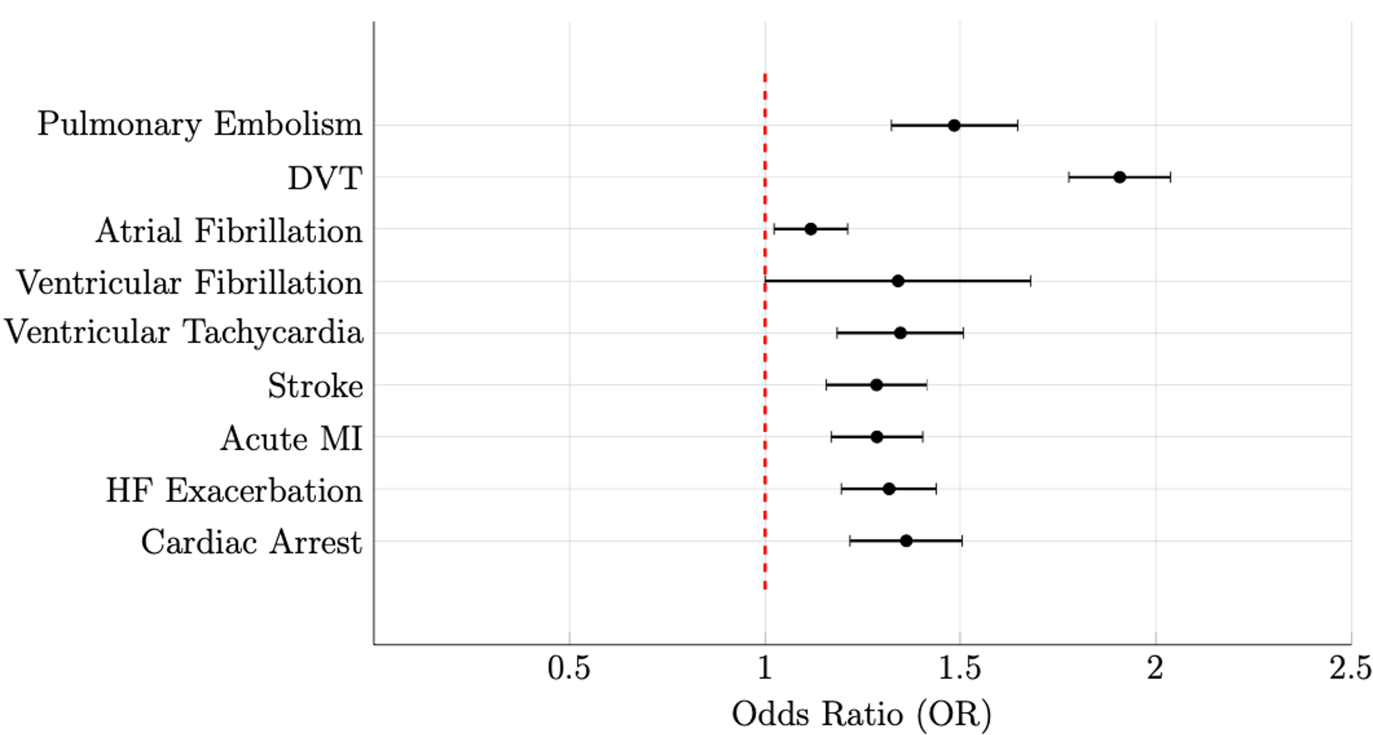
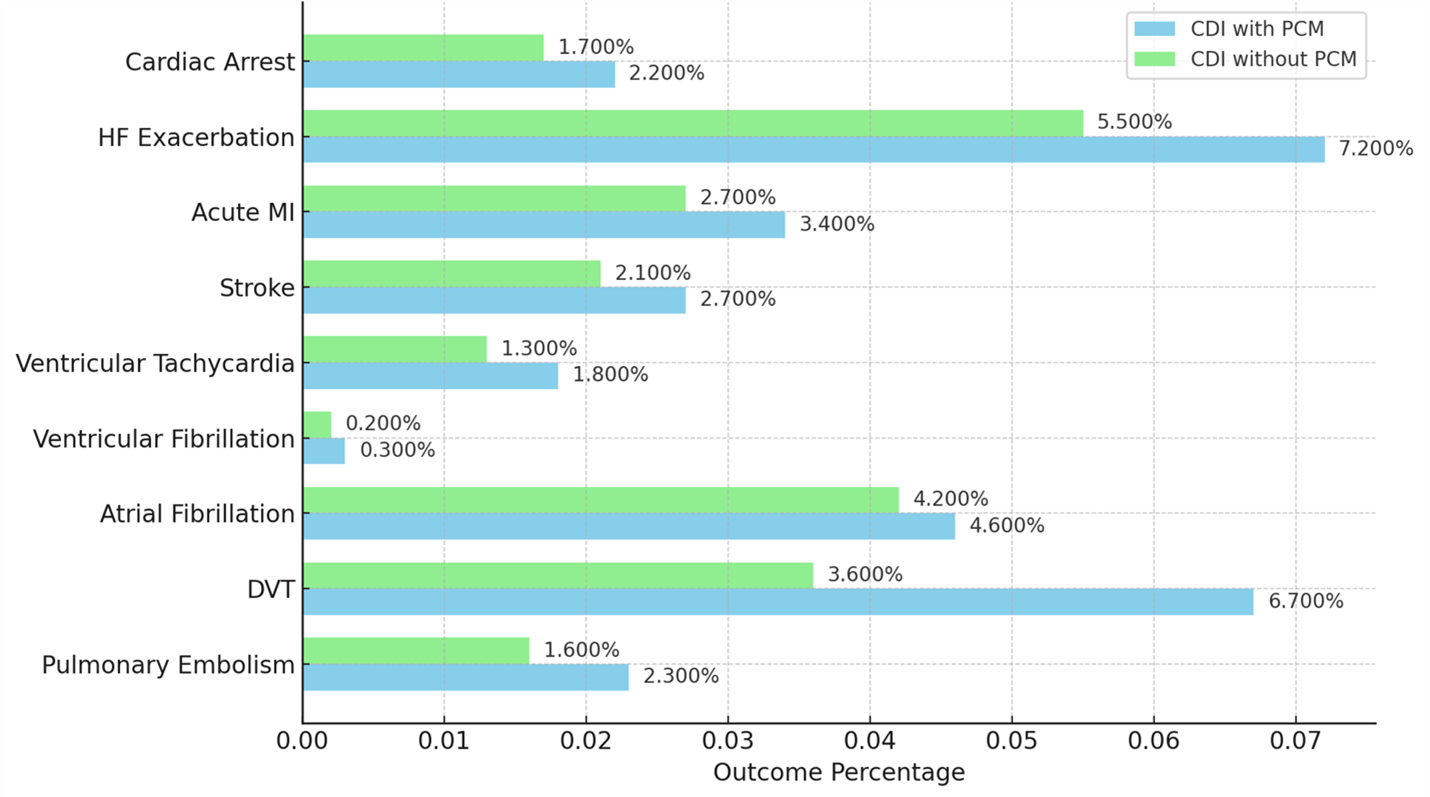
Results: Patients with PCM exhibited significantly higher odds of adverse cardiovascular outcomes compared to those without malnutrition. The odds of developing PE were 1.49 times higher (OR: 1.485, 95% CI: 1.323-1.666, p < 0.001), and the odds of DVT were markedly elevated as well (OR: 1.91, 95% CI: 1.778-2.047, p < 0.001). Additionally, malnourished patients had a slightly increased risk of AF (OR: 1.12, 95% CI: 1.023-1.219, p = 0.013) and a 34% higher risk of VF (OR: 1.34, 95% CI: 1.000-1.794, p = 0.049). The odds of VT were also significantly higher in this group (OR: 1.35, 95% CI: 1.184-1.529, p < 0.001). The risk of acute MI was increased (OR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.169-1.415, p < 0.001), as was the risk of HF exacerbation (OR: 1.32, 95% CI: 1.218-1.425, p < 0.001). Stroke risk was similarly elevated (OR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.156-1.427, p < 0.001), and the odds of cardiac arrest were significantly higher in malnourished patients (OR: 1.36, 95% CI: 1.217-1.522, p < 0.001).
Discussion: PCM significantly worsens one-year cardiovascular and thromboembolic outcomes in patients with CDI. These findings underscore the need for targeted nutritional interventions and close monitoring of high-risk patients with PCM to mitigate adverse outcomes.
Disclosures:
Rashid Abdel-Razeq, MD1, Chidera Onwuzo, MBBS2, Somtochukwu Onwuzo, MD3, Kojo-Frimpong B. Awuah, MD4, Mohamad-Noor Abu-Hammour, MD5, Barish Eren, MD1, Antoine Boustany, MD6, Lana Dardari, MD7, Basil Jalamneh, MD1. P1282 - Impact of Protein-Calorie Malnutrition on One-Year Cardiovascular and Thromboembolic Outcomes in Patients With <i>Clostridioides difficile</i> Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 2SUNY Upstate Medical University Hospital, Syracuse, NY; 3Allegheny Center for Digestive Health, Pittsburgh, PA; 4Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA; 5Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 6Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, FL; 7Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Westlake, OH
Introduction: Malnutrition has significant health implications, contributing to increased morbidity, mortality, and prolonged hospitalizations in patients. Its impact in patients with Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) has not been thoroughly evaluated. In this study, we aim to examine the relationship between PCM and once-year cardiovascular and thromboembolic outcomes in patients with CDI within the United States.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of deidentified, aggregate patient data from TriNetX research network. The cohort compromised patients 18 years of age or older with a diagnosis of CDI. Within this cohort, patients with and without PCM were identified. Primary outcomes were one-year cardiovascular and thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism (PE), deep vein thrombosis (DVT), atrial fibrillation (AF), ventricular fibrillation (VF), ventricular tachycardia (VT), myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure exacerbation, stroke, and cardiac arrest. Variables including age, sex, comorbidities, and other factors known to confound the association between PCM and the composite outcomes underwent 1:1 propensity score matching. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was also utilized to analyze the matched cohorts.
Results: Patients with PCM exhibited significantly higher odds of adverse cardiovascular outcomes compared to those without malnutrition. The odds of developing PE were 1.49 times higher (OR: 1.485, 95% CI: 1.323-1.666, p < 0.001), and the odds of DVT were markedly elevated as well (OR: 1.91, 95% CI: 1.778-2.047, p < 0.001). Additionally, malnourished patients had a slightly increased risk of AF (OR: 1.12, 95% CI: 1.023-1.219, p = 0.013) and a 34% higher risk of VF (OR: 1.34, 95% CI: 1.000-1.794, p = 0.049). The odds of VT were also significantly higher in this group (OR: 1.35, 95% CI: 1.184-1.529, p < 0.001). The risk of acute MI was increased (OR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.169-1.415, p < 0.001), as was the risk of HF exacerbation (OR: 1.32, 95% CI: 1.218-1.425, p < 0.001). Stroke risk was similarly elevated (OR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.156-1.427, p < 0.001), and the odds of cardiac arrest were significantly higher in malnourished patients (OR: 1.36, 95% CI: 1.217-1.522, p < 0.001).
Discussion: PCM significantly worsens one-year cardiovascular and thromboembolic outcomes in patients with CDI. These findings underscore the need for targeted nutritional interventions and close monitoring of high-risk patients with PCM to mitigate adverse outcomes.

Figure: Figure1: Comparison of cardiovascular and thrombotic outcomes in patients diagnosed with CDI with PCM and patients with CDI but no PCM

Figure: Figure2: Forest plot graph comparing odds ratio for cardiovascular and thrombotic outcomes in patients with CDI with and without PCM
Disclosures:
Rashid Abdel-Razeq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chidera Onwuzo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Somtochukwu Onwuzo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kojo-Frimpong B. Awuah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad-Noor Abu-Hammour indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Barish Eren indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Antoine Boustany indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lana Dardari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basil Jalamneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rashid Abdel-Razeq, MD1, Chidera Onwuzo, MBBS2, Somtochukwu Onwuzo, MD3, Kojo-Frimpong B. Awuah, MD4, Mohamad-Noor Abu-Hammour, MD5, Barish Eren, MD1, Antoine Boustany, MD6, Lana Dardari, MD7, Basil Jalamneh, MD1. P1282 - Impact of Protein-Calorie Malnutrition on One-Year Cardiovascular and Thromboembolic Outcomes in Patients With <i>Clostridioides difficile</i> Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
