Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1580 - Evaluating the Effectiveness of Antiviral Therapy in Reducing the Incidence of de novo Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Compensated HCV-Related Cirrhosis: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Has Audio

Vanessa Pamela Salolin Vargas, MD
Gastroenterology Consultants
Mexico City, Distrito Federal, Mexico
Presenting Author(s)
Vanessa Pamela Salolin-Vargas, MD1, Mauricio Alejandro Saldana-Ruiz, MD2, Wilfor Diaz Fernandez, MD3, Huber Padilla-Zambrano, MD4, Mario Saul Lira-Castañeda, MS5, Sritha Moram, MS6, Karim Ali, MD7, Krishna Kolluri, MS8, Anna Rachel Shajee, MD9, Mohamad Omar Diab, MD10
1Gastroenterology Consultants, Mexico City, Distrito Federal, Mexico; 2Gastroenterology Consultants, Monterrey, Nuevo Leon, Mexico; 3Mayo Clinic, Boston, MA; 4Gastroenterology Consultants, Cartagena, Bolivar, Colombia; 5Gastroenterology Consultants, Durango, Durango, Mexico; 6Gastroenterology Consultants, Athens, GA; 7Gastroenterology Consultants, Cambridge, England, United Kingdom; 8Gastroenterology Consultants, Philadelphia, PA; 9Gastroenterology Consultants, Katowice, Slaskie, Poland; 10Canyon Vista Medical Center, Sierra Vista, AZ
Introduction: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infection is a major global health concern with Chronic hepatitis C infection being a leading cause of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) worldwide. The introduction of Direct-acting antiviral therapy (DAA) revolutionised management of HCV through a Sustained virologic response and a decrease in liver-related mortality. Our objective was to Evaluate the effect of DAA therapy on the incidence of de novo HCC, focusing specifically on patients with compensated HCV-related cirrhosis.
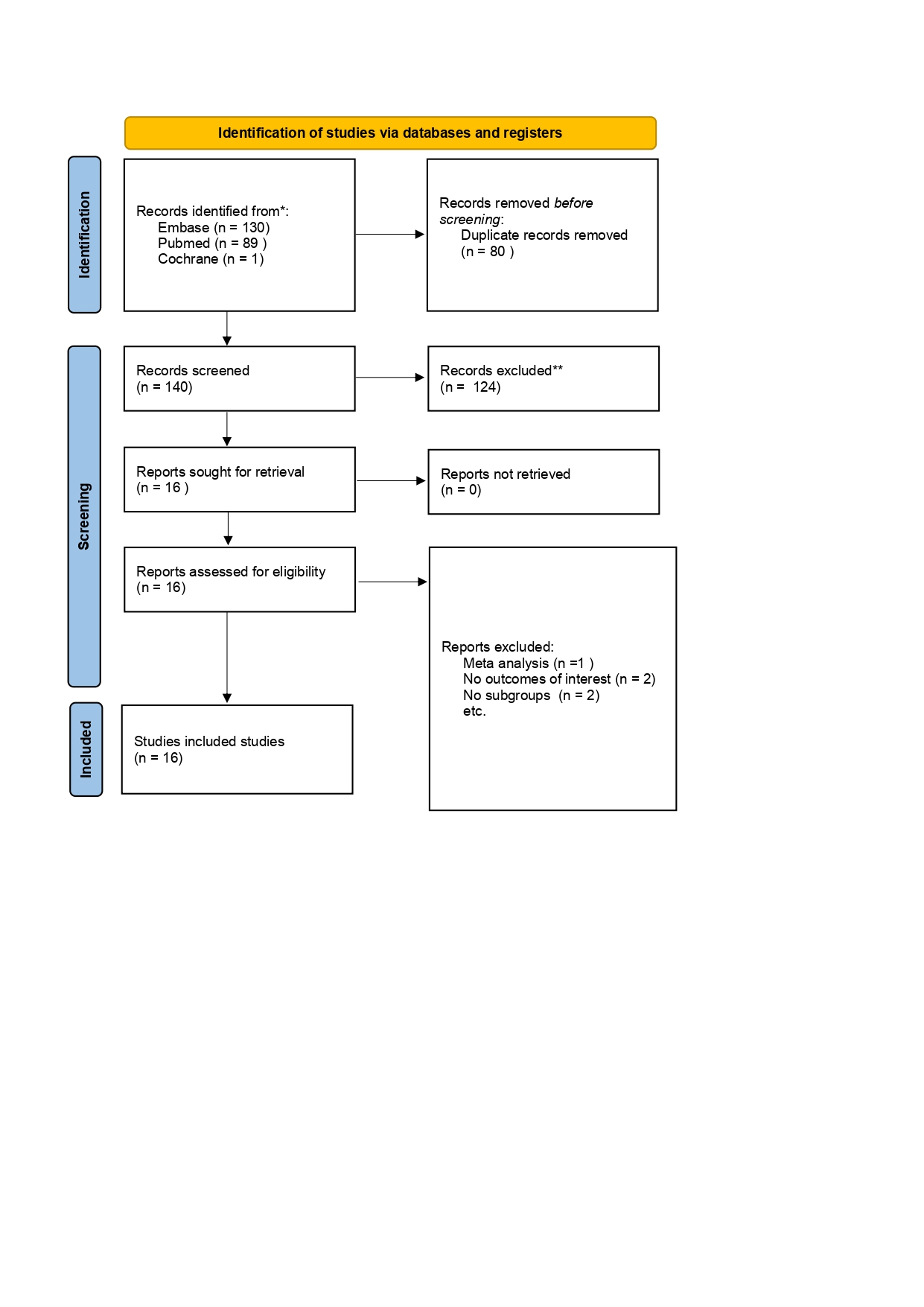
Methods: A comprehensive search was performed on PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library for studies comparing the incidence of HCC in patients with compensated cirrhosis due to hepatitis C who received DAA therapy. The main outcomes were incidence rate of de novo HCC rate per 100 PY, cirrhosis status, DAA-treated patients. Statistical analyses were performed using Review Manager 5.4.1 (Cochrane Collaboration). The I2 test was employed for heterogeneity assessment, while the risk of bias was evaluated utilizing ROBINS-I
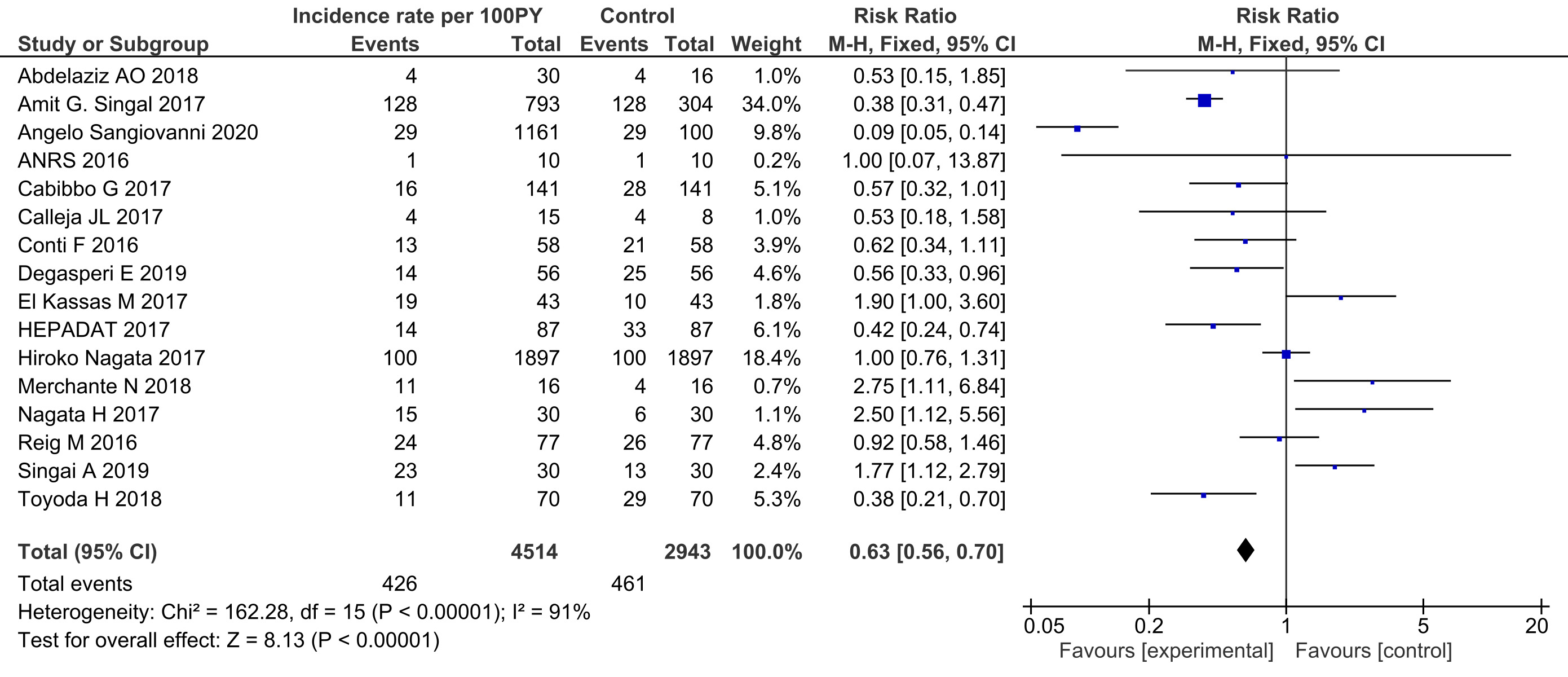
Results: We included 4,636 patients from 16 observational studies in this meta-analysis. In comparison, the incidence rate of de novo HCC was reduced in the treatment group with a risk ratio (RR) of 0.63 (95% CI 0.56–0.70, p < 0.00001) per 100PY. While incidence and mortality rates in DAA-treated patients were found to be statistically significant. Subgroup analyses based on factors such as sex, age, cirrhosis status (including progression, stability, or regression), Child-Pugh classification, AFP, ALT, and AST levels showed no statistically significant differences.
Discussion: The use of DAAs in patients with chronic hepatitis C has generated considerable debate regarding their impact on the development and recurrence of HCC. Initial observational studies and case series raised concerns about decreased rates of de novo HCC following DAA therapy, particularly in patients with advanced cirrhosis. Despite these reassuring data, the controversy persists due to heterogeneity in study populations, timing of antiviral initiation, and follow-up durations, underscoring the importance of further research to clearly delineate the interplay between antiviral therapy and hepatocarcinogenesis.
Disclosures:
Vanessa Pamela Salolin-Vargas, MD1, Mauricio Alejandro Saldana-Ruiz, MD2, Wilfor Diaz Fernandez, MD3, Huber Padilla-Zambrano, MD4, Mario Saul Lira-Castañeda, MS5, Sritha Moram, MS6, Karim Ali, MD7, Krishna Kolluri, MS8, Anna Rachel Shajee, MD9, Mohamad Omar Diab, MD10. P1580 - Evaluating the Effectiveness of Antiviral Therapy in Reducing the Incidence of <i>de novo</i> Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Compensated HCV-Related Cirrhosis: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Gastroenterology Consultants, Mexico City, Distrito Federal, Mexico; 2Gastroenterology Consultants, Monterrey, Nuevo Leon, Mexico; 3Mayo Clinic, Boston, MA; 4Gastroenterology Consultants, Cartagena, Bolivar, Colombia; 5Gastroenterology Consultants, Durango, Durango, Mexico; 6Gastroenterology Consultants, Athens, GA; 7Gastroenterology Consultants, Cambridge, England, United Kingdom; 8Gastroenterology Consultants, Philadelphia, PA; 9Gastroenterology Consultants, Katowice, Slaskie, Poland; 10Canyon Vista Medical Center, Sierra Vista, AZ
Introduction: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infection is a major global health concern with Chronic hepatitis C infection being a leading cause of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) worldwide. The introduction of Direct-acting antiviral therapy (DAA) revolutionised management of HCV through a Sustained virologic response and a decrease in liver-related mortality. Our objective was to Evaluate the effect of DAA therapy on the incidence of de novo HCC, focusing specifically on patients with compensated HCV-related cirrhosis.
Methods: A comprehensive search was performed on PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library for studies comparing the incidence of HCC in patients with compensated cirrhosis due to hepatitis C who received DAA therapy. The main outcomes were incidence rate of de novo HCC rate per 100 PY, cirrhosis status, DAA-treated patients. Statistical analyses were performed using Review Manager 5.4.1 (Cochrane Collaboration). The I2 test was employed for heterogeneity assessment, while the risk of bias was evaluated utilizing ROBINS-I
Results: We included 4,636 patients from 16 observational studies in this meta-analysis. In comparison, the incidence rate of de novo HCC was reduced in the treatment group with a risk ratio (RR) of 0.63 (95% CI 0.56–0.70, p < 0.00001) per 100PY. While incidence and mortality rates in DAA-treated patients were found to be statistically significant. Subgroup analyses based on factors such as sex, age, cirrhosis status (including progression, stability, or regression), Child-Pugh classification, AFP, ALT, and AST levels showed no statistically significant differences.
Discussion: The use of DAAs in patients with chronic hepatitis C has generated considerable debate regarding their impact on the development and recurrence of HCC. Initial observational studies and case series raised concerns about decreased rates of de novo HCC following DAA therapy, particularly in patients with advanced cirrhosis. Despite these reassuring data, the controversy persists due to heterogeneity in study populations, timing of antiviral initiation, and follow-up durations, underscoring the importance of further research to clearly delineate the interplay between antiviral therapy and hepatocarcinogenesis.

Figure: HCC incidence rate per 100PY.

Figure: PRISMA flow-chart.
Disclosures:
Vanessa Pamela Salolin-Vargas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mauricio Alejandro Saldana-Ruiz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wilfor Diaz Fernandez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Huber Padilla-Zambrano indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mario Saul Lira-Castañeda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sritha Moram indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karim Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishna Kolluri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anna Rachel Shajee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Omar Diab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vanessa Pamela Salolin-Vargas, MD1, Mauricio Alejandro Saldana-Ruiz, MD2, Wilfor Diaz Fernandez, MD3, Huber Padilla-Zambrano, MD4, Mario Saul Lira-Castañeda, MS5, Sritha Moram, MS6, Karim Ali, MD7, Krishna Kolluri, MS8, Anna Rachel Shajee, MD9, Mohamad Omar Diab, MD10. P1580 - Evaluating the Effectiveness of Antiviral Therapy in Reducing the Incidence of <i>de novo</i> Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Compensated HCV-Related Cirrhosis: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
