Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4534 - Clinical Utility and Application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Algorithms in the Accurate Diagnosis of Appendicitis - A Meta-Analysis

- AG
Aryan Gupta
bangalore medical college and research institute
Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Presenting Author(s)
1Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 2bangalore medical college and research institute, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 3Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4Ramaiah medical college, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 5Maulana Azad Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 6BGS Global Institute of Medical Sciences, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 7ramaiah medical college, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Introduction:
Appendicitis is a relatively common acute abdominal condition, requiring prompt and accurate diagnosis to prevent complications. Traditional diagnostic methods often lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary surgeries. Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms have emerged as promising tools for enhancing diagnostic accuracy. By analyzing vast amounts of clinical data, imaging studies in particular, AI can identify subtle patterns and indicators of appendicitis. It’s utility mainly lies in reducing the diagnostic errors and optimizing the improving patient care in the domain of appendicitis.
Methods:
The review conducted follows the PRISMA guidelines and major medical databases, which include PUBMED, Google Scholar and Science-Direct, were extensively searched using a comprehensive search term to identify and retrieve available articles. The articles that assessed diagnostic potential, ie, Accuracy and Area Under The Curve(AUC), were included in the final analysis.
The data was analysed using the Meta, Metadata and the Metafor packages of R Studio. The pooled accuracy and AUC were assessed in the study to estimate the diagnostic potential of AI-assisted imaging in the diagnosis of Appendicitis.The random effects model via the linear (mixed-effects) model framework was considered for statistical analysis.
Results:
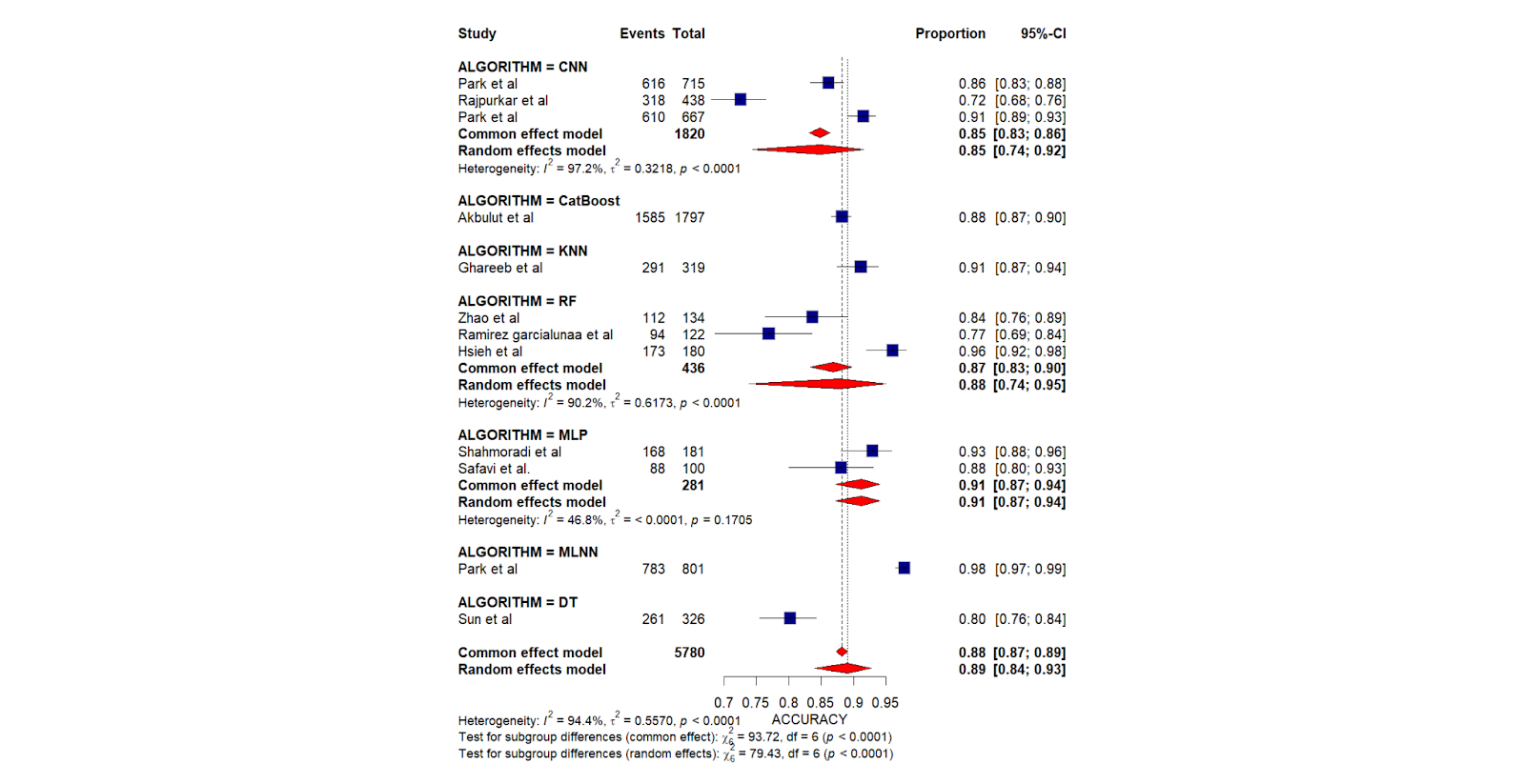
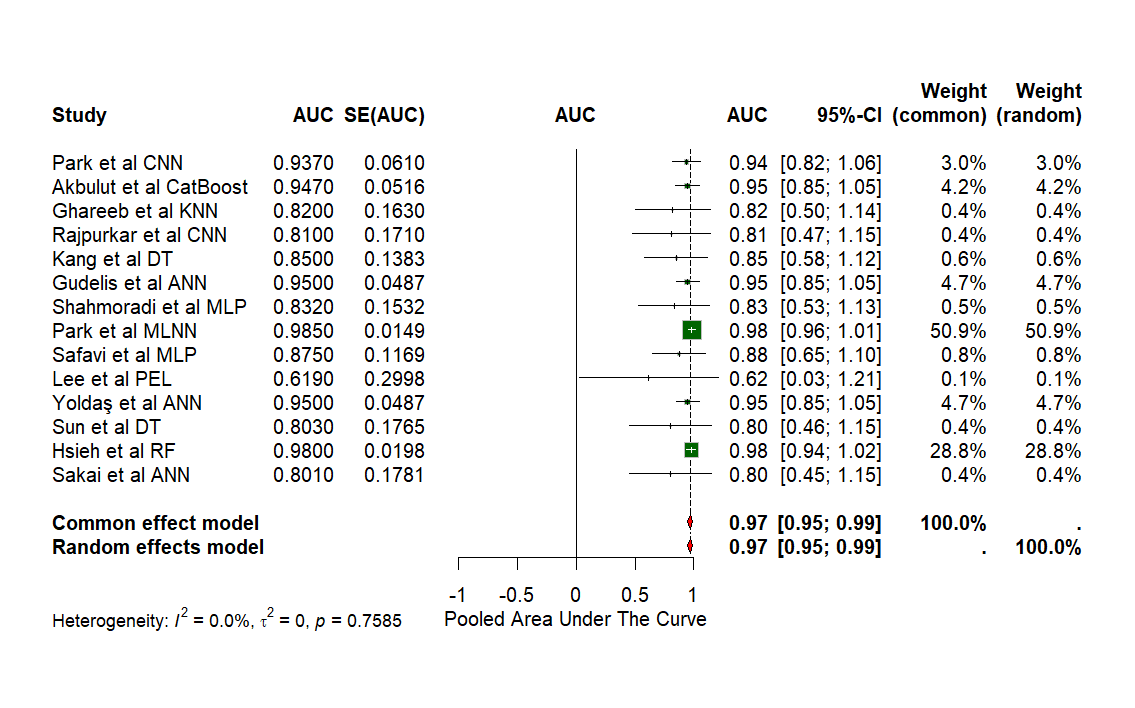
The study included a total of 19 studies with a total of 7767 images that assessed the presence of appendicitis. The pooled accuracy for the diagnosis of appendicitis was assessed to be 0.89 [0.84;0.93, CI 95%, p< 0.0001]. The pooled AUC emerged to be 0.97 [0.95;0.99, CI 95%, p=0.7585].
Discussion: Through this meta-analysis, the Artificial Intelligence algorithms have been analysed and evaluated to be clinically effective in the detection of appendicitis, as evident by their high accuracy.
Disclosures:
Era Gupta, 1, Aryan Gupta, 2, Kushal Prasad, 1, Omar Oudit, DO3, Vinay Chandramouli Bellur, 4, Shekhar Kalra, 5, Vardhini Ganesh Iyer, 6, Ananya Prasad, 7. P4534 - Clinical Utility and Application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Algorithms in the Accurate Diagnosis of Appendicitis - A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
