Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4578 - Qualitative Comparison of Air-Charged and Solid-State HRAM Catheter Normative Values in Healthy Subjects
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Has Audio
- KA
Kamran Ayub, MD, MRCP
Southwest Gastroenterology, a Division of GI Partners of Illinois
New Lenox , IL
Presenting Author(s)
Kamran Ayub, MD, MRCP1, Satish SC. Rao, MD, PhD, FACG2, Allan Weston, MD, FACG3, Karlo Fidel, MD2, Delaram Asadi, MD2, Danielle Long, BS2
1Southwest Gastroenterology, a Division of GI Partners of Illinois, Oak Lawn, IL; 2Augusta University Medical Center, Augusta, GA; 3Digestive Health Center of the Four States, LLC, Joplin, MO
Introduction: While high-resolution anorectal manometry (HRAM) is essential for evaluating anorectal function, absolute pressure values can vary substantially depending on the catheter type. Air-charged and solid-state catheters differ in construction, transduction mechanism, and calibration method—each influencing recorded values. This variability necessitates catheter-specific interpretation. As a secondary objective of the ILLUMINATE study, we compared normative data from a novel 10-Channel Air-Charged Disposable High-Resolution Anorectal Manometry (HRAM) Catheter (Solar™ catheter) to published values from solid-state systems to assess qualitative agreement and highlight device-specific considerations.
Methods: The ILLUMINATE study was a prospective, multi-center, open-label trial wherein all subjects underwent standardized HRAM using a novel 10-channel air-charged disposable HRAM catheter per IAPWG protocol and London Classification, and a subset also underwent testing with the solid-state (UniTip™) catheter (n=30). Parameters collected included: anal resting pressure, squeeze pressure, cough pressure, and functional anal canal length. Values were descriptively compared to published normative datasets from solid-state catheter systems.
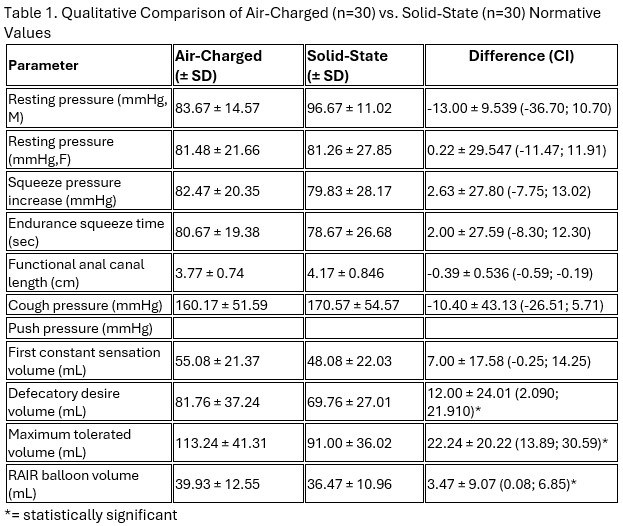
Results: There were 30 subjects (3 males, 37 females; mean age = 39 ± 9 years) who underwent both novel 10-channel air-charged disposable catheter and solid-state catheter ARM studies. Anal resting pressures recorded with the air-charged catheter were approximately equivalent to solid-state reference values. Functional anal canal length measurements were consistent across technologies as well. See Table 1 details.
Discussion: Minor differences were observed between air-charged and solid-state HRAM catheters, but in general physiologic trends were preserved across systems. These findings underscore the importance of using catheter-specific normative values when interpreting HRAM results and reinforce that direct numeric comparison between devices may not be valid. The novel 10-Channel Air-Charged Disposable High-Resolution Anorectal Manometry (HRAM) Catheter demonstrated consistent performance and clinical utility within its calibrated reference range.
Disclosures:
Kamran Ayub, MD, MRCP1, Satish SC. Rao, MD, PhD, FACG2, Allan Weston, MD, FACG3, Karlo Fidel, MD2, Delaram Asadi, MD2, Danielle Long, BS2. P4578 - Qualitative Comparison of Air-Charged and Solid-State HRAM Catheter Normative Values in Healthy Subjects, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Southwest Gastroenterology, a Division of GI Partners of Illinois, Oak Lawn, IL; 2Augusta University Medical Center, Augusta, GA; 3Digestive Health Center of the Four States, LLC, Joplin, MO
Introduction: While high-resolution anorectal manometry (HRAM) is essential for evaluating anorectal function, absolute pressure values can vary substantially depending on the catheter type. Air-charged and solid-state catheters differ in construction, transduction mechanism, and calibration method—each influencing recorded values. This variability necessitates catheter-specific interpretation. As a secondary objective of the ILLUMINATE study, we compared normative data from a novel 10-Channel Air-Charged Disposable High-Resolution Anorectal Manometry (HRAM) Catheter (Solar™ catheter) to published values from solid-state systems to assess qualitative agreement and highlight device-specific considerations.
Methods: The ILLUMINATE study was a prospective, multi-center, open-label trial wherein all subjects underwent standardized HRAM using a novel 10-channel air-charged disposable HRAM catheter per IAPWG protocol and London Classification, and a subset also underwent testing with the solid-state (UniTip™) catheter (n=30). Parameters collected included: anal resting pressure, squeeze pressure, cough pressure, and functional anal canal length. Values were descriptively compared to published normative datasets from solid-state catheter systems.
Results: There were 30 subjects (3 males, 37 females; mean age = 39 ± 9 years) who underwent both novel 10-channel air-charged disposable catheter and solid-state catheter ARM studies. Anal resting pressures recorded with the air-charged catheter were approximately equivalent to solid-state reference values. Functional anal canal length measurements were consistent across technologies as well. See Table 1 details.
Discussion: Minor differences were observed between air-charged and solid-state HRAM catheters, but in general physiologic trends were preserved across systems. These findings underscore the importance of using catheter-specific normative values when interpreting HRAM results and reinforce that direct numeric comparison between devices may not be valid. The novel 10-Channel Air-Charged Disposable High-Resolution Anorectal Manometry (HRAM) Catheter demonstrated consistent performance and clinical utility within its calibrated reference range.

Figure: Table 1. Qualitative Comparison of Air-Charged (n=30) vs. Solid-State (n=30) Normative Values
Disclosures:
Kamran Ayub: Laborie Medical Technologies – Grant/Research Support.
Satish Rao: Laborie Medical Technologies – Grant/Research Support. Vibrant Ltd – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Allan Weston: Laborie Medical Technologies – Grant/Research Support.
Karlo Fidel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Delaram Asadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danielle Long indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kamran Ayub, MD, MRCP1, Satish SC. Rao, MD, PhD, FACG2, Allan Weston, MD, FACG3, Karlo Fidel, MD2, Delaram Asadi, MD2, Danielle Long, BS2. P4578 - Qualitative Comparison of Air-Charged and Solid-State HRAM Catheter Normative Values in Healthy Subjects, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
