Monday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P2481 - Lymphocytic Colitis Triggered by C. difficile Infection in the Setting of Anti-TNFα Therapy
- EO
Emilee Ohman, BS
University of North Dakota, School of Medicine and Health Sciences
Fargo, ND
Presenting Author(s)
1University of North Dakota, School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Fargo, ND; 2University of North Dakota, School of Medicine and Health Sciences, West Fargo, ND; 3Sanford Health, West Fargo, ND; 4Sanford Health, Fargo, ND
Introduction:
Lymphocytic colitis (LC) is a subtype of microscopic colitis (MC) characterized by lymphocytic infiltration of the lamina propria that presents with chronic diarrhea and abdominal pain. The etiology is not well defined, but may be secondary to a disruption of the colonic epithelial barrier that triggers an autoimmune reaction. Gastrointestinal infections, such as C. difficile, can cause these epithelial disruptions and microbiome changes. The management of this disease includes supportive measures and budesonide therapy. Increasingly, remission has been found to occur with the use of anti-TNFa agents in MC patients. This report will describe a case of lymphocytic colitis developed months after a first time C. difficile infection in a patient already on chronic anti-TNFa therapy.
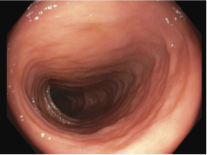
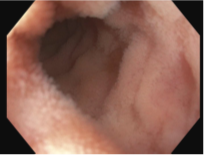
Case Description/Methods: A 48-year-old female with rheumatoid arthritis on certolizumab and methotrexate presented with a 2-month history of persistent watery diarrhea, 30-pound weight loss, and severe hypotension. She had been diagnosed with a first time C. difficile infection at the onset of diarrhea and completed a course of fidaxomicin for 10 days. She continued to have diarrhea, and subsequent testing for C. difficile came back negative multiple times. Abdominal CT, celiac disease serology, CMV testing, and enteric stool panel all returned negative on admission. Initial laboratory studies included hemoglobin 10.4, MCV 96.0, potassium 3.2, and albumin 3.3. Fecal calprotectin was significantly elevated at 172, suggesting pathology not better explained by irritable bowel syndrome. The patient underwent both EGD and colonoscopy, with EGD showing signs of gastritis. The colonic mucosa appeared diffusely edematous (Figure 1), and the terminal ileum was unremarkable (Figure 2). Random colon biopsies were consistent with a diagnosis of lymphocytic colitis. The patient was started on budesonide therapy with subsequent improvement of symptoms. She was continued on her home regimen of certolizumab and methotrexate at discharge.
Discussion: Microscopic colitis symptoms can have considerable impacts on quality of life. While treatment with budesonide remains the preferred initial therapy for MC, new research has shown promising evidence for remission in refractory cases with anti-TNF-alpha biologic agents. Here we describe a unique case of LC developed after a first time C. difficile infection in a patient on anti-TNF-alpha therapy, highlighting the importance of keeping MC on a differential in immunocompromised patients.
Disclosures:
Emilee Ohman, BS1, Hussam Almasri, MD2, Rajendra Potluri, MD3, Dinesh Bande, MD3, John Bassett, MD4. P2481 - Lymphocytic Colitis Triggered by <i>C. difficile</i> Infection in the Setting of Anti-TNFα Therapy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
