Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Infections and Microbiome
P5556 - Impact of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Ghrelin Levels and BMI: Single-Arm Meta-Analysis With Leave-One-Out Sensitivity Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Ashesh Das, MBBS
KPC Medical College and Hospital , Kolkata, India
Kolkata, West Bengal, India
Presenting Author(s)
Ashesh Das, MBBS1, M. Rafiqul Islam, 2, Venkata Dileep Kumar Veldi, MBBS3, Param Darpan Sheth, 4, Shayan Mahapatra, MD5, Chandana Priya Digumurthy, MBBS6, Ruheen Shariff, MBBS7, Kavya Shah, MBBS8, Arpitha Sirichandana. Baggu, MBBS9, Devagna P.. Mehta, MBBS10, Rahul Akkapeddi, MBBS11
1KPC Medical College and Hospital , Kolkata, India, Kolkata, West Bengal, India; 2Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh, Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh; 3Gayatri Vidya Parishad Institute of Health care and Medical Technology, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India; 4JSS Medical College , JSS academy of higher education and research, Mysuru, Karnataka, India; 5Aiken Regional Medical Center, Graniteville, SC; 6Apollo institute of medical sciences and research, Chittoor , Andhra Pradesh ,India, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India; 7NARAYANA MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, Greater Noida West, Uttar Pradesh, India; 8GMERS Medical College and Hospital, Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India; 9Sri Padmavathi medical college for women,SVIMS,Tirupati, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India; 10GCS Medical College, Ahmedabad, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 11Gandhi Medical College & Hospital, Secunderabad, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Introduction: A persistent Helicobacter pylori infection suppresses the production of gastric ghrelin, which may restrict appetite and growth. Although eradication therapy may increase endocrine production, its effect on body weight is still up for debate, which feeds worries about obesity and hopes for better nutrition. We combined longitudinal studies that assessed body-mass index (BMI) and circulating ghrelin levels before and after confirmed eradication in order to provide clarity.
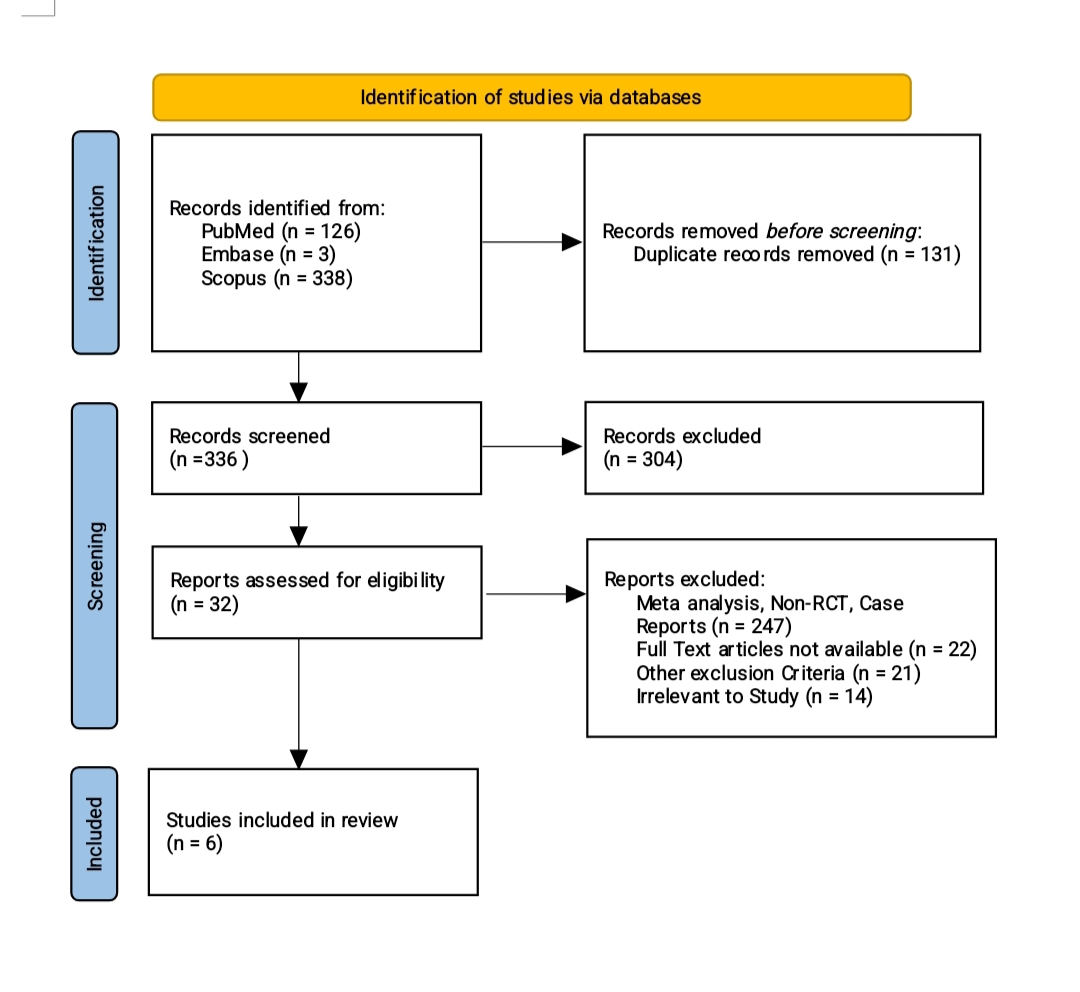
Methods: A systematic search of MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus and CENTRAL were searched for trials or cohorts reporting paired pre/post ghrelin or BMI ≥ 4 weeks after confirmed eradication through May 2025. Two reviewers screened, extracted means ± SD and judged bias with RoB 2 or Newcastle-Ottawa. Pooled mean differences were generated with DL random effects model; heterogeneity was summarised by τ² and I². Forest plots displayed effect sizes, while leave-one-out plots located influential studies. Data analysis was done using R (v4.4.3) with 'meta' package.
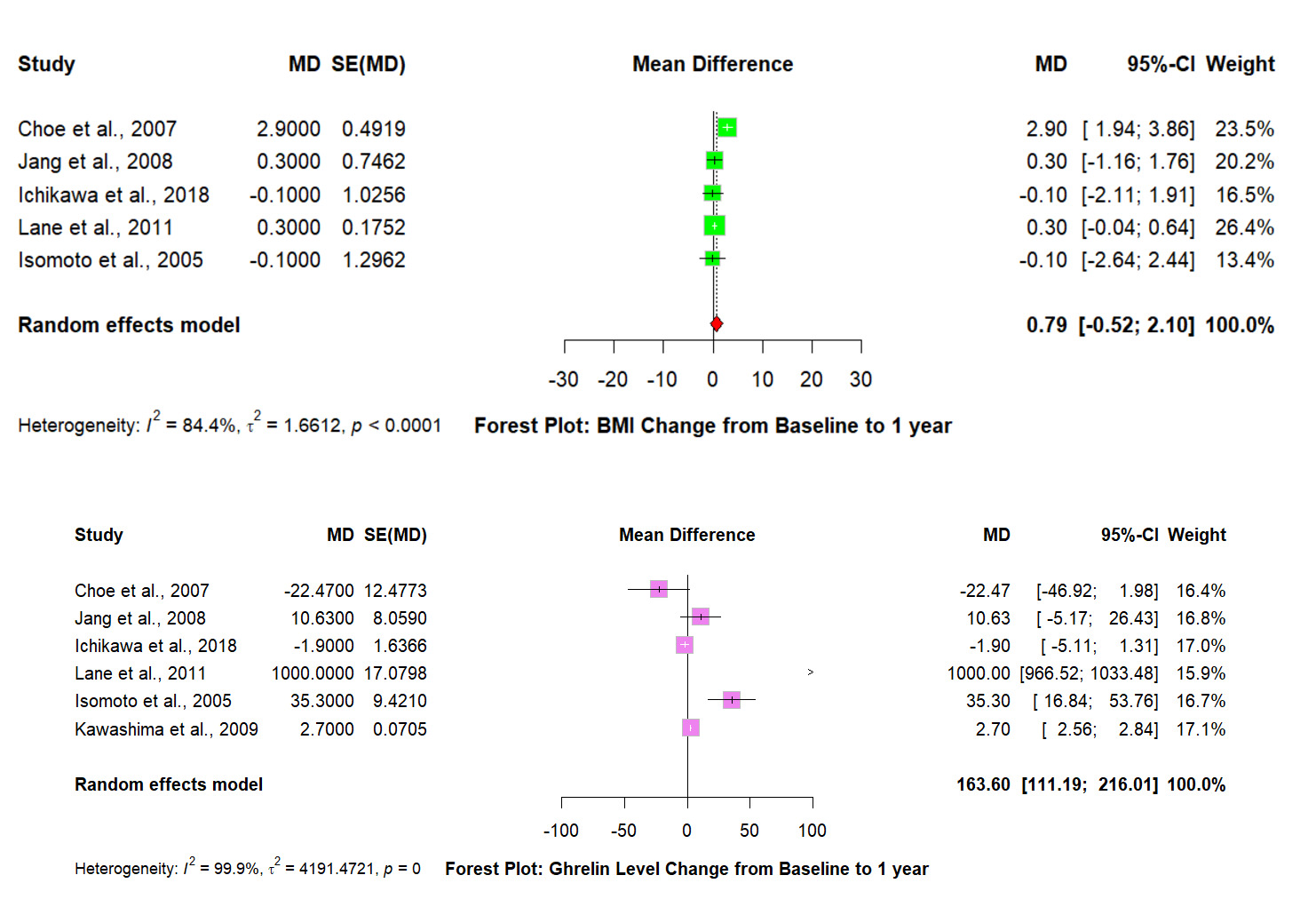
Results: Six studies, comprising 1002 participants, assessed changes in ghrelin levels and BMI following H. pylori eradication.For BMI change, the random-effects model showed a non-significant mean difference (MD) of 0.79 (95% CI: -0.52 to 2.10) with high heterogeneity (I² = 84.4%, τ² = 1.66). Leave-one-out analysis revealed that excluding Choe et al. (2007) reduced heterogeneity to 0% and yielded an MD of 0.28 (95% CI: -0.04 to 0.61).For ghrelin levels, eradication significantly increased levels with an MD of 163.60 (95% CI: 111.19 to 216.01) but showed extreme heterogeneity (I² = 99.9%, τ² = 4191.47). Sensitivity analysis found all studies contributed to high heterogeneity except Lane et al (2011) whose exclusion lowered I² to 83.9% and resulted in an MD of 3.42 (95% CI: -2.80 to 9.64).
Discussion: These results suggest H. pylori eradication raises ghrelin and may modestly raise BMI, but heterogeneity limits firm conclusions. The rebound confirms infection suppression yet seldom yields clinically relevant weight gain. Paediatric studies showed small increases, whereas adult community trials and dialysis cohorts were weight-neutral, explaining most dispersion. Leave-one-out influence plots demonstrated that removing such context-specific outliers normalised heterogeneity and centred BMI effects on null. Clinically, eradication seems to restore endocrine balance without promoting obesity, though longer, better-powered trials across diverse metabolic profiles are needed.
Disclosures:
Ashesh Das, MBBS1, M. Rafiqul Islam, 2, Venkata Dileep Kumar Veldi, MBBS3, Param Darpan Sheth, 4, Shayan Mahapatra, MD5, Chandana Priya Digumurthy, MBBS6, Ruheen Shariff, MBBS7, Kavya Shah, MBBS8, Arpitha Sirichandana. Baggu, MBBS9, Devagna P.. Mehta, MBBS10, Rahul Akkapeddi, MBBS11. P5556 - Impact of <i>Helicobacter pylori</i> Eradication on Ghrelin Levels and BMI: Single-Arm Meta-Analysis With Leave-One-Out Sensitivity Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1KPC Medical College and Hospital , Kolkata, India, Kolkata, West Bengal, India; 2Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh, Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh; 3Gayatri Vidya Parishad Institute of Health care and Medical Technology, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India; 4JSS Medical College , JSS academy of higher education and research, Mysuru, Karnataka, India; 5Aiken Regional Medical Center, Graniteville, SC; 6Apollo institute of medical sciences and research, Chittoor , Andhra Pradesh ,India, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India; 7NARAYANA MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, Greater Noida West, Uttar Pradesh, India; 8GMERS Medical College and Hospital, Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India; 9Sri Padmavathi medical college for women,SVIMS,Tirupati, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India; 10GCS Medical College, Ahmedabad, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 11Gandhi Medical College & Hospital, Secunderabad, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Introduction: A persistent Helicobacter pylori infection suppresses the production of gastric ghrelin, which may restrict appetite and growth. Although eradication therapy may increase endocrine production, its effect on body weight is still up for debate, which feeds worries about obesity and hopes for better nutrition. We combined longitudinal studies that assessed body-mass index (BMI) and circulating ghrelin levels before and after confirmed eradication in order to provide clarity.
Methods: A systematic search of MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus and CENTRAL were searched for trials or cohorts reporting paired pre/post ghrelin or BMI ≥ 4 weeks after confirmed eradication through May 2025. Two reviewers screened, extracted means ± SD and judged bias with RoB 2 or Newcastle-Ottawa. Pooled mean differences were generated with DL random effects model; heterogeneity was summarised by τ² and I². Forest plots displayed effect sizes, while leave-one-out plots located influential studies. Data analysis was done using R (v4.4.3) with 'meta' package.
Results: Six studies, comprising 1002 participants, assessed changes in ghrelin levels and BMI following H. pylori eradication.For BMI change, the random-effects model showed a non-significant mean difference (MD) of 0.79 (95% CI: -0.52 to 2.10) with high heterogeneity (I² = 84.4%, τ² = 1.66). Leave-one-out analysis revealed that excluding Choe et al. (2007) reduced heterogeneity to 0% and yielded an MD of 0.28 (95% CI: -0.04 to 0.61).For ghrelin levels, eradication significantly increased levels with an MD of 163.60 (95% CI: 111.19 to 216.01) but showed extreme heterogeneity (I² = 99.9%, τ² = 4191.47). Sensitivity analysis found all studies contributed to high heterogeneity except Lane et al (2011) whose exclusion lowered I² to 83.9% and resulted in an MD of 3.42 (95% CI: -2.80 to 9.64).
Discussion: These results suggest H. pylori eradication raises ghrelin and may modestly raise BMI, but heterogeneity limits firm conclusions. The rebound confirms infection suppression yet seldom yields clinically relevant weight gain. Paediatric studies showed small increases, whereas adult community trials and dialysis cohorts were weight-neutral, explaining most dispersion. Leave-one-out influence plots demonstrated that removing such context-specific outliers normalised heterogeneity and centred BMI effects on null. Clinically, eradication seems to restore endocrine balance without promoting obesity, though longer, better-powered trials across diverse metabolic profiles are needed.

Figure: Figure Showing Mean Change in BMI and Ghrelin

Figure: Prisma Flowchart
Disclosures:
Ashesh Das indicated no relevant financial relationships.
M. Rafiqul Islam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Venkata Dileep Kumar Veldi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Param Darpan Sheth indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shayan Mahapatra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chandana Priya Digumurthy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ruheen Shariff indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kavya Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arpitha Baggu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Devagna Mehta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rahul Akkapeddi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashesh Das, MBBS1, M. Rafiqul Islam, 2, Venkata Dileep Kumar Veldi, MBBS3, Param Darpan Sheth, 4, Shayan Mahapatra, MD5, Chandana Priya Digumurthy, MBBS6, Ruheen Shariff, MBBS7, Kavya Shah, MBBS8, Arpitha Sirichandana. Baggu, MBBS9, Devagna P.. Mehta, MBBS10, Rahul Akkapeddi, MBBS11. P5556 - Impact of <i>Helicobacter pylori</i> Eradication on Ghrelin Levels and BMI: Single-Arm Meta-Analysis With Leave-One-Out Sensitivity Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
