Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4547 - IL-23 p19 Blockade Triples 12-Week Clinical and Mucosal Remission Without Added Adverse Events in Moderate-to-Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 4 Randomized Controlled Trials
.jpg)
Ashesh Das, MBBS
KPC Medical College and Hospital , Kolkata, India
Kolkata, West Bengal, India
Presenting Author(s)
1KPC Medical College and Hospital , Kolkata, India, Kolkata, West Bengal, India; 2Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA; 3Gayatri Vidya Parishad Institute of Health care and Medical Technology, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India; 4Lokmanya Tilak Municipal Medical College and General Hospital, Mumbai, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India; 5Stanley Medical College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India; 6Osmania General Hospital and Medical College, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 7SUNY Downstate Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 8Duke University, Durham, NC
Introduction:
IL-23 is pivotal in chronic gut inflammation, yet the impact of isolating its p19 subunit in ulcerative colitis (UC) has only just emerged. Phase-3 trials of mirikizumab, risankizumab and guselkumab each reported strong induction efficacy, but the unified signal and safety picture were unknown. We present the first pooled analysis of all Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) quantifying the class effect of IL-23 p19 blockade, addressing a critical evidence gap amid an increasingly crowded advanced-therapy landscape.
Methods:
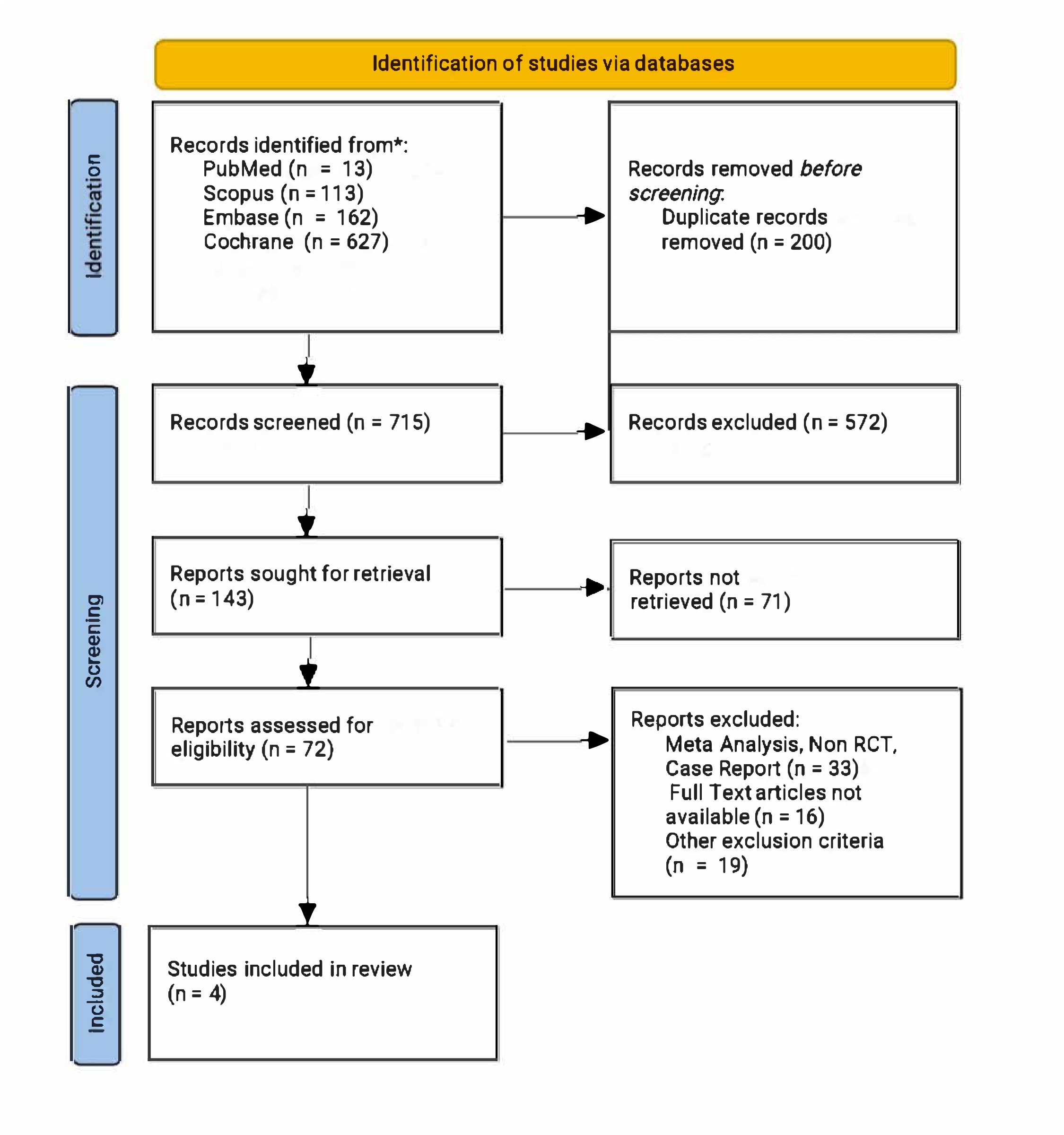
A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and Cochrane Library identified RCTs comparing IL23 p19 blockade drugs versus placebo in managing UC through May 2025. Data were analysed using RevMan 4.2.1. Pooled risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using Mantel-Haenszel methods. Random- or fixed-effects models were applied based on heterogeneity (Higgins’ I²). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Risk of bias was assessed using RoB 2.0.
Results:
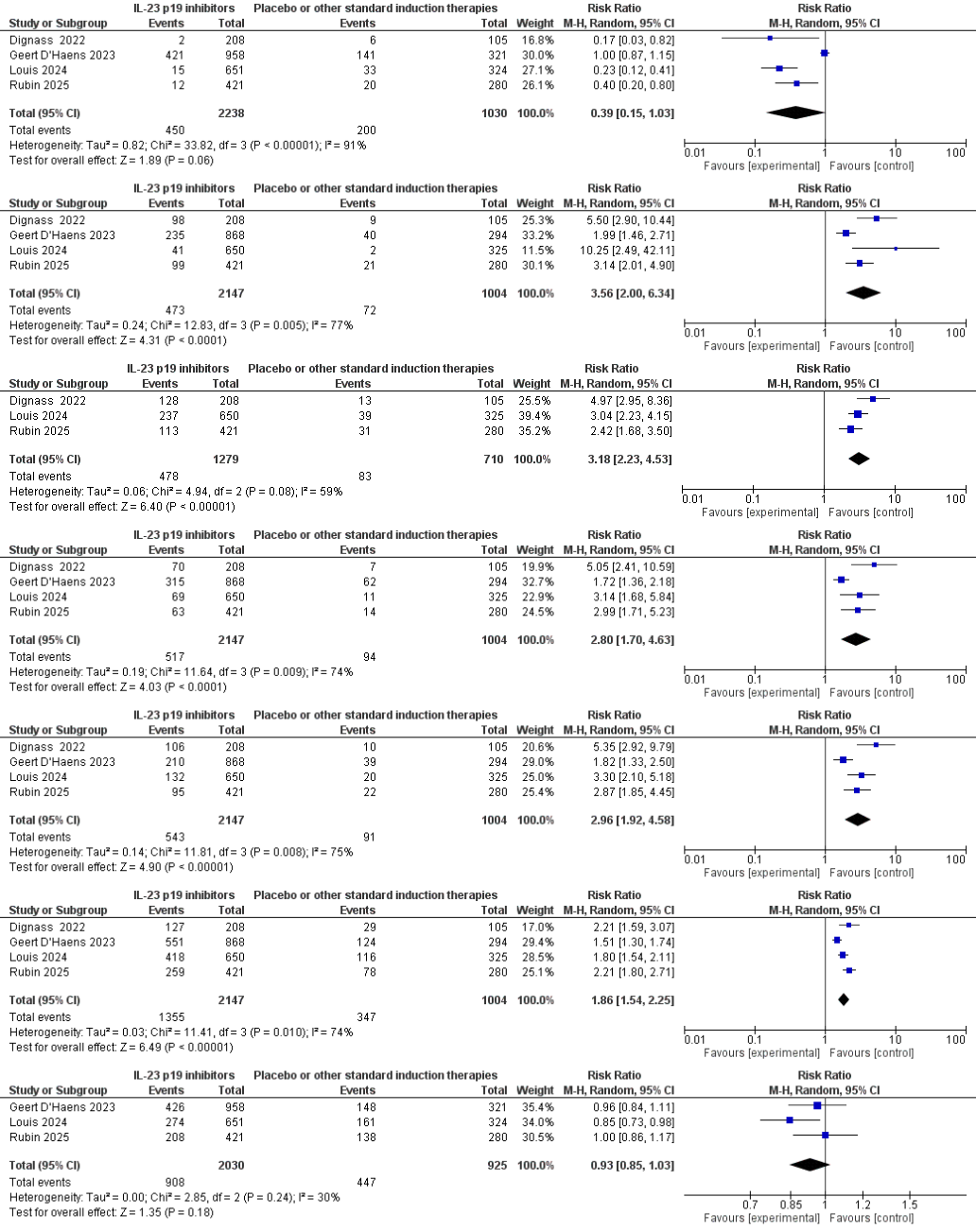
Among 3 151 participants in four RCTs of IL-23 p19 inhibitors (guselkumab, mirikizumab, risankizumab), 12-week induction therapy nearly tripled clinical remission (25.3 % vs 9.1 %; RR 2.96, 95 % CI 1.92–4.58) and markedly enhanced endoscopic outcomes—improvement (37.4 % vs 11.7 %; RR 3.18, 2.23–4.53), remission (24.1 % vs 9.4 %; RR 2.80, 1.70–4.63) and composite mucosal healing (22 % vs 7 %; RR 3.56, 2.00–6.34). Overall adverse-event frequency remained similar to placebo (44.7 % vs 48.3 %; RR 0.93, 0.85–1.03), while serious events were numerically lower (2.0 % vs 6.5 %; RR 0.39, 0.15–1.03), underscoring a favorable benefit–risk profile for IL-23 p19 blockade in moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis.
Discussion:
This meta-analysis shows that IL-23 p19 inhibitors nearly triple 12-week clinical and mucosal remission while matching placebo on overall adverse events and hinting at fewer serious harms. Benefit consistency across three molecules, despite moderate heterogeneity, confirms a reproducible class effect and positions IL-23 blockade as a potent alternative to TNF-α or JAK inhibition. Clinically, early mucosal healing predicts durable remission, colectomy avoidance and lower neoplasia risk, making the magnitude of endoscopic benefit highly relevant. Our synthesis therefore delivers timely evidence for guideline updates, informs payer decisions, and equips clinicians to adopt this novel therapeutic class with confidence.
Disclosures:
Ashesh Das, MBBS1, Hafsa Shahid, MD2, Venkata Dileep Kumar Veldi, MBBS3, Urvashi Bharia, 4, Noorul Hidhaya, MBBS5, Saketh S. Mandiga, MBBS6, Daniel Razgonyaev, 7, Naga Sai Akhil Reddy Gogula, MBBS8. P4547 - IL-23 p19 Blockade Triples 12-Week Clinical and Mucosal Remission Without Added Adverse Events in Moderate-to-Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 4 Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
