Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P4174 - Real-World Clinical Study for Effectiveness and Safety of Vonoprazan-Based Dual Therapy Versus PPI-Based Triple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Sanjay Bandyopadhyay, MD
ILS Dumdum Hospital, Kolkata
Kolkata, West Bengal, India
Presenting Author(s)
Sanjay Bandyopadhyay, MD1, Debjoy Sau, MD1, Abhishek Banerjee, MD2, Dr Gajanan Panchal, MD3, Dr Maneesha Khalse, MD3, Dr. Kamlesh Patel, MD3
1ILS Dumdum Hospital, Kolkata, Kolkata, West Bengal, India; 2Manipal Hospital Broadway, Salt Lake, Kolkata, Kolkata, West Bengal, India; 3Lupin Ltd., Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
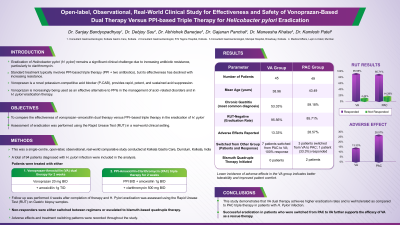
Introduction: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) remains a significant clinical challenge due to increasing antibiotic resistance, particularly to clarithromycin. Vonoprazan, a potassium-competitive acid blocker, is gaining use as an effective alternative to proton pump inhibitors for acid-related conditions and H. pylori treatment. This study assesses the effectiveness of vonoprazan–amoxicillin (VA) dual therapy versus proton pump inhibitor (PPI)-amoxicillin-clarithromycin (PAC) based triple therapy in routine clinical practice, based on H. pylori eradication assessed by the rapid urease test (RUT).
Methods: This was a single-centre, open-label, observational, real-world comparative study conducted at Kolkata Gastro Care, Dumdum, Kolkata, India, from July 2024 to March 2025. Data from 94 patients diagnosed with H. pylori infection were analysed. Patients received either VA (vonoprazan 20 mg BID + amoxicillin 1g TID) or PAC (PPI BID + amoxicillin 1g BID + clarithromycin 500 mg BID). Follow-up was performed at 4 weeks using RUT on the biopsy sample. Patients unresponsive to initial therapy were either switched between regimens or escalated to bismuth quadruple therapy. Adverse effects and switching patterns were observed.
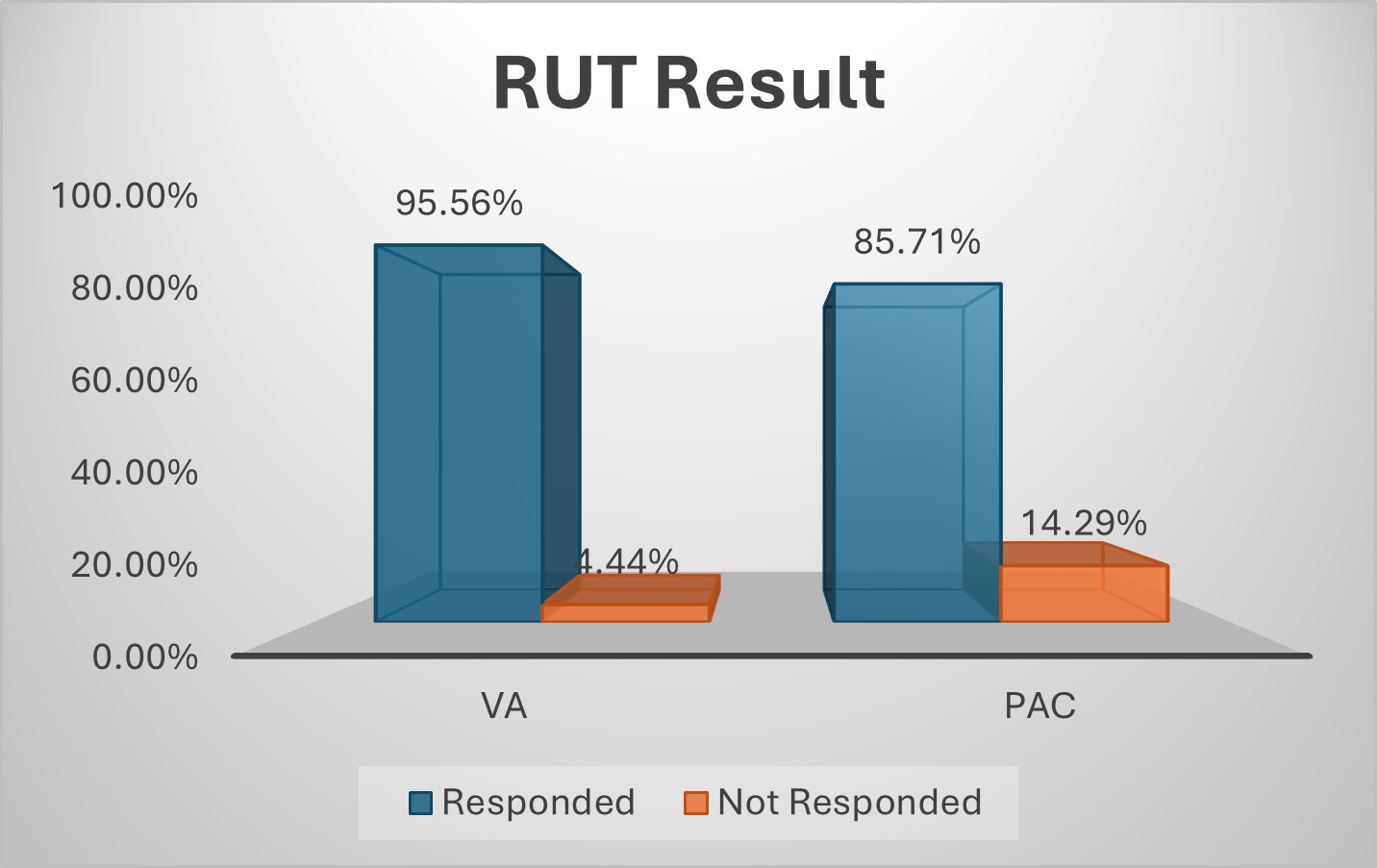
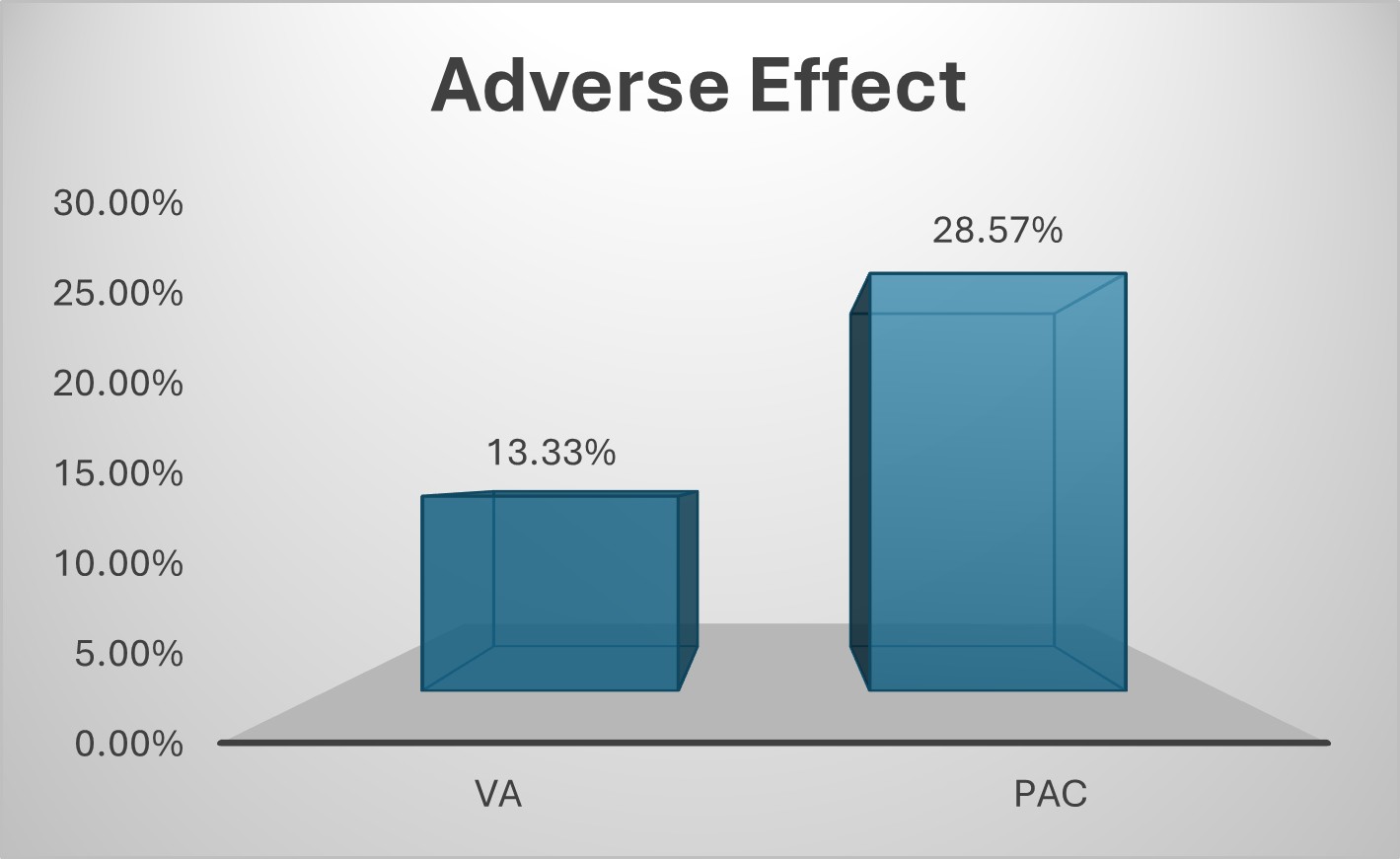
Results: A total of 94 patients with H. pylori infection were analyzed, with 45 initiated on VA dual therapy and 49 on PAC regimen. The mean age (SD) was 38.96 (±13.18) years in VA and 43.49 (±11.34) years in PAC group. Chronic gastritis was the most frequent diagnosis across both groups (53.33% in VA, 59.18% in PAC). Post-treatment, negative RUT cases were numerically higher in VA than those in PAC regimen (95.56% vs 85.71%). Adverse effects were reported in 13.33% of patients in VA group versus 28.57% of those in PAC group. One out of three patients (6.67%) who switched from VA to PAC while all 7 patients (14.29%) from PAC to VA achieved a response. Third-line bismuth quadruple therapy was initiated in two patients from the VA group.
Discussion: This study demonstrates that VA dual therapy achieves higher eradication rates and is better tolerated than PAC regimen in patients with H. pylori infection. Additionally, the lower incidence of adverse effects in the VA group suggests improved patient tolerability. The successful eradication of H. pylori infection in patients switched from PAC to VA further supports its efficacy as a rescue therapy.
Disclosures:
Sanjay Bandyopadhyay, MD1, Debjoy Sau, MD1, Abhishek Banerjee, MD2, Dr Gajanan Panchal, MD3, Dr Maneesha Khalse, MD3, Dr. Kamlesh Patel, MD3. P4174 - Real-World Clinical Study for Effectiveness and Safety of Vonoprazan-Based Dual Therapy Versus PPI-Based Triple Therapy for <i>Helicobacter Pylori</i> Eradication, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1ILS Dumdum Hospital, Kolkata, Kolkata, West Bengal, India; 2Manipal Hospital Broadway, Salt Lake, Kolkata, Kolkata, West Bengal, India; 3Lupin Ltd., Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Introduction: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) remains a significant clinical challenge due to increasing antibiotic resistance, particularly to clarithromycin. Vonoprazan, a potassium-competitive acid blocker, is gaining use as an effective alternative to proton pump inhibitors for acid-related conditions and H. pylori treatment. This study assesses the effectiveness of vonoprazan–amoxicillin (VA) dual therapy versus proton pump inhibitor (PPI)-amoxicillin-clarithromycin (PAC) based triple therapy in routine clinical practice, based on H. pylori eradication assessed by the rapid urease test (RUT).
Methods: This was a single-centre, open-label, observational, real-world comparative study conducted at Kolkata Gastro Care, Dumdum, Kolkata, India, from July 2024 to March 2025. Data from 94 patients diagnosed with H. pylori infection were analysed. Patients received either VA (vonoprazan 20 mg BID + amoxicillin 1g TID) or PAC (PPI BID + amoxicillin 1g BID + clarithromycin 500 mg BID). Follow-up was performed at 4 weeks using RUT on the biopsy sample. Patients unresponsive to initial therapy were either switched between regimens or escalated to bismuth quadruple therapy. Adverse effects and switching patterns were observed.
Results: A total of 94 patients with H. pylori infection were analyzed, with 45 initiated on VA dual therapy and 49 on PAC regimen. The mean age (SD) was 38.96 (±13.18) years in VA and 43.49 (±11.34) years in PAC group. Chronic gastritis was the most frequent diagnosis across both groups (53.33% in VA, 59.18% in PAC). Post-treatment, negative RUT cases were numerically higher in VA than those in PAC regimen (95.56% vs 85.71%). Adverse effects were reported in 13.33% of patients in VA group versus 28.57% of those in PAC group. One out of three patients (6.67%) who switched from VA to PAC while all 7 patients (14.29%) from PAC to VA achieved a response. Third-line bismuth quadruple therapy was initiated in two patients from the VA group.
Discussion: This study demonstrates that VA dual therapy achieves higher eradication rates and is better tolerated than PAC regimen in patients with H. pylori infection. Additionally, the lower incidence of adverse effects in the VA group suggests improved patient tolerability. The successful eradication of H. pylori infection in patients switched from PAC to VA further supports its efficacy as a rescue therapy.

Figure: Figure 1: Comparison between VA and PAC according to RUT Result

Figure: Figure 2: Comparison between VA and PAC according to Adverse Effect
Disclosures:
Sanjay Bandyopadhyay indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Debjoy Sau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhishek Banerjee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dr Gajanan Panchal: Lupin Ltd. – Employee.
Dr Maneesha Khalse: Lupin Ltd. – Employee.
Dr. Kamlesh Patel: Lupin Ltd. – Employee.
Sanjay Bandyopadhyay, MD1, Debjoy Sau, MD1, Abhishek Banerjee, MD2, Dr Gajanan Panchal, MD3, Dr Maneesha Khalse, MD3, Dr. Kamlesh Patel, MD3. P4174 - Real-World Clinical Study for Effectiveness and Safety of Vonoprazan-Based Dual Therapy Versus PPI-Based Triple Therapy for <i>Helicobacter Pylori</i> Eradication, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
