Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P4165 - Efficacy and Safety of 14-Day Vonoprazan-Based Quadruple Therapy vs PPI-Based Regimens for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- YH
Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD
The University of Toledo
Toledo, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD1, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD1, Sana Rabeeah, MD1, Umberto Battistin, MD1, Hayder Alamily, MD2, Mhd Kutaiba Albuni, MD3, Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD4, Shahem Abbarh, MD5, Mulham Alom, MD6, Muhamad Oum, MD7, Obada Daaboul, MD8, Elias Battikh, MD9, Bisher Sawaf, MD10, Amine Rakab, MD11, Yaseen Alastal, MD12
1The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 2University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, CO; 3Department of Internal Medicine, TriHealth Inc., Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH; 4University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH; 5Georgetown University MedStar Health, Baltimore, WA; 6Internal Medicine, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, IL; 7Saint Agnes Medical Center, Fresno CA, Fresno, CA; 8Southern Illinois University, Springfield, IL; 9John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Toledo, OH; 10University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 11Division of Medical Education, Weill Cornell Medicine, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 12University of Toledo, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is essential for treating gastric ulcers and reducing the risk of gastric cancer. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have traditionally been a key component of triple therapy for H. pylori eradication; however, their efficacy has diminished globally due to the rising prevalence of antibiotic resistance. In contrast, novel potassium-competitive acid blockers, such as vonoprazan-based quadruple therapy (VPZ-Q-14), significantly enhance the success of first-line H. pylori eradication by providing potent suppression of gastric acid secretion. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of VPZ-Q-14 compared to conventional PPI-based regimens for H. pylori eradication.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase through October 2024 to identify randomized clinical trials involving adult patients with Helicobacter pylori who were treated with vonoprazan-based therapies. Trials assessing the safety and efficacy of VPZ-Q-14 and PPI-based regimens for H. pylori eradication were included. The primary outcomes were H. pylori eradication (intention-to-treat) and adverse events. A random-effects model was applied for statistical analysis using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) software, and pooled odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated.
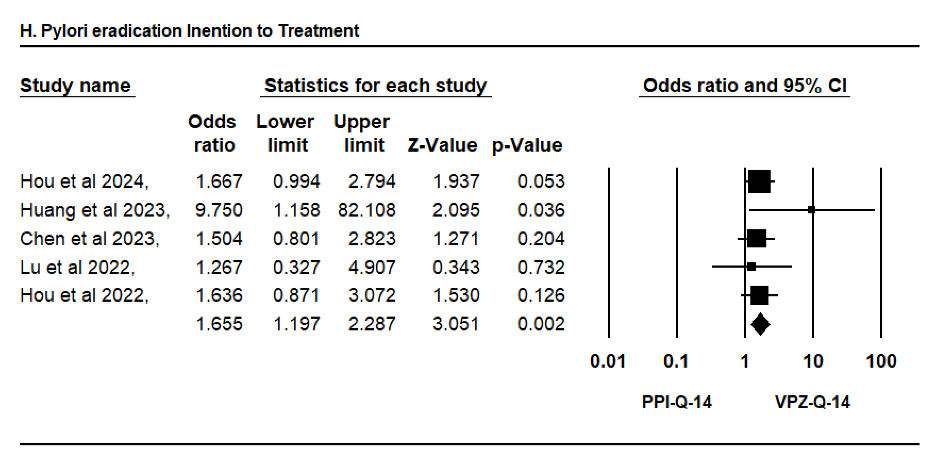
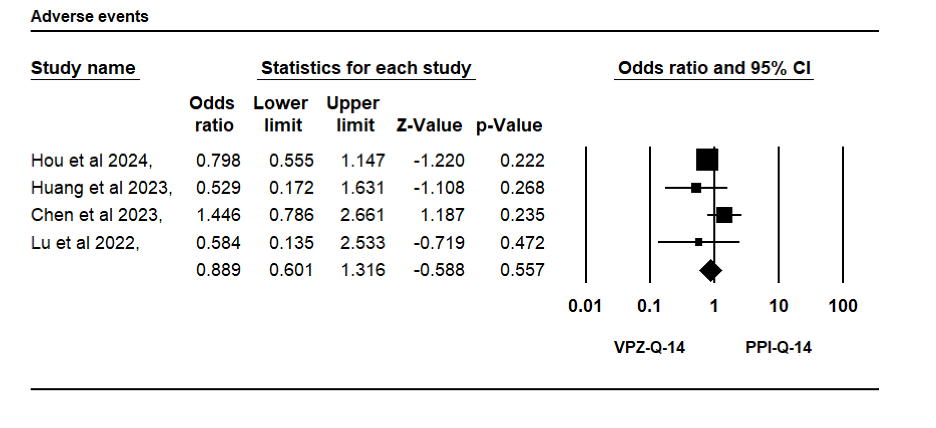
Results: Five clinical trials involving 1,816 patients were included in the analysis. VPZ-Q-14 demonstrated superior H. pylori eradication compared to PPI-based therapies (OR = 1.66, 95% CI: 1.20–2.29, p = 0.002) (Figure 1). In contrast, the incidence of adverse events with 14-day VPZ-based therapy was comparable to that of 14-day PPI-based therapies (OR = 0.89, 95% CI: 0.60–1.32, p = 0.56) (Figure 2).
Discussion: VPZ-A-14 demonstrated a significantly higher H. pylori eradication rate compared to PPI-based therapies. The incidence of adverse events was similar between the two treatment groups. These results suggest that 14-day vonoprazan-based therapy is as effective and safe as 14-day PPI-based therapy for H. pylori eradication, with a superior eradication rate and comparable adverse events.
Disclosures:
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD1, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD1, Sana Rabeeah, MD1, Umberto Battistin, MD1, Hayder Alamily, MD2, Mhd Kutaiba Albuni, MD3, Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD4, Shahem Abbarh, MD5, Mulham Alom, MD6, Muhamad Oum, MD7, Obada Daaboul, MD8, Elias Battikh, MD9, Bisher Sawaf, MD10, Amine Rakab, MD11, Yaseen Alastal, MD12. P4165 - Efficacy and Safety of 14-Day Vonoprazan-Based Quadruple Therapy vs PPI-Based Regimens for <i>Helicobacter pylori</i> Eradication: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 2University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, CO; 3Department of Internal Medicine, TriHealth Inc., Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH; 4University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH; 5Georgetown University MedStar Health, Baltimore, WA; 6Internal Medicine, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, IL; 7Saint Agnes Medical Center, Fresno CA, Fresno, CA; 8Southern Illinois University, Springfield, IL; 9John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Toledo, OH; 10University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 11Division of Medical Education, Weill Cornell Medicine, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 12University of Toledo, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is essential for treating gastric ulcers and reducing the risk of gastric cancer. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have traditionally been a key component of triple therapy for H. pylori eradication; however, their efficacy has diminished globally due to the rising prevalence of antibiotic resistance. In contrast, novel potassium-competitive acid blockers, such as vonoprazan-based quadruple therapy (VPZ-Q-14), significantly enhance the success of first-line H. pylori eradication by providing potent suppression of gastric acid secretion. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of VPZ-Q-14 compared to conventional PPI-based regimens for H. pylori eradication.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase through October 2024 to identify randomized clinical trials involving adult patients with Helicobacter pylori who were treated with vonoprazan-based therapies. Trials assessing the safety and efficacy of VPZ-Q-14 and PPI-based regimens for H. pylori eradication were included. The primary outcomes were H. pylori eradication (intention-to-treat) and adverse events. A random-effects model was applied for statistical analysis using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) software, and pooled odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated.
Results: Five clinical trials involving 1,816 patients were included in the analysis. VPZ-Q-14 demonstrated superior H. pylori eradication compared to PPI-based therapies (OR = 1.66, 95% CI: 1.20–2.29, p = 0.002) (Figure 1). In contrast, the incidence of adverse events with 14-day VPZ-based therapy was comparable to that of 14-day PPI-based therapies (OR = 0.89, 95% CI: 0.60–1.32, p = 0.56) (Figure 2).
Discussion: VPZ-A-14 demonstrated a significantly higher H. pylori eradication rate compared to PPI-based therapies. The incidence of adverse events was similar between the two treatment groups. These results suggest that 14-day vonoprazan-based therapy is as effective and safe as 14-day PPI-based therapy for H. pylori eradication, with a superior eradication rate and comparable adverse events.

Figure: Figure 1: Forest plot comparing H. pylori eradication rates (intention-to-treat) between VPZ-Q-14 and PPI-based regimens.

Figure: Figure 2: Forest plot comparing the incidence of adverse events between VPZ-Q-14 and PPI-based regimens.
Disclosures:
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yusuf Omar Hallak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sana Rabeeah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umberto Battistin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hayder Alamily indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mhd Kutaiba Albuni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hasan Al-Obaidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahem Abbarh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mulham Alom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhamad Oum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Obada Daaboul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elias Battikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amine Rakab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yaseen Alastal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD1, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD1, Sana Rabeeah, MD1, Umberto Battistin, MD1, Hayder Alamily, MD2, Mhd Kutaiba Albuni, MD3, Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD4, Shahem Abbarh, MD5, Mulham Alom, MD6, Muhamad Oum, MD7, Obada Daaboul, MD8, Elias Battikh, MD9, Bisher Sawaf, MD10, Amine Rakab, MD11, Yaseen Alastal, MD12. P4165 - Efficacy and Safety of 14-Day Vonoprazan-Based Quadruple Therapy vs PPI-Based Regimens for <i>Helicobacter pylori</i> Eradication: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
