Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0295 - The Role of miR-122 in Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis: A Systematic Review of Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Potential

.jpg)
Diksha Sanjana Pasnoor, MBBS
Kamineni Academy of Medical Sciences and Research Centre
Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Presenting Author(s)
1Kamineni Academy of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 2NRI Medical College and General Hospital, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India; 3Deccan College of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 4University of Michigan-Flint, Flint, MI; 5Duke University, Durham, NC; 6Cape Fear Valley Hospital, Fayetteville, NC; 7Baton Rouge General Medical Center, Baton Rogue, LA; 8Sanford Bemidji Medical Center, Bemidji, MN; 9Rutgers Monmouth Medical Center, Long Branch, NJ; 10Institute of Medical Sciences and SUM Hospital, Bhubaneswar, Orissa, India; 11Independent Outcomes Researcher, Atlanta, GA
Introduction:
Liver metastasis significantly compromises the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC), which remains a leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), particularly miR-122, regulate gene expression, influencing tumor growth, migration, and invasion. This makes them promising candidates for both diagnostic and therapeutic strategies targeting colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRLM). This systematic review synthesizes current evidence on miR-122 in CRLM, emphasizing its role in CRC progression, the formation of liver metastases, and potential clinical applications.
Methods:
A thorough literature search was conducted using PubMed and Google Scholar and snowballing technique to identify studies focused on miR-122 in CRLM, with specific keywords guiding the search.The search included studies published from 2013 to 2024. We incorporated original research articles that addressed the molecular mechanisms, therapeutic applications, and miRNA expression profiles in CRLM. Data were extracted on patient populations, methodologies, primary outcomes, therapeutic implications, and study designs. Quality assessment was conducted according to PRISMA guidelines to ensure methodological rigor.
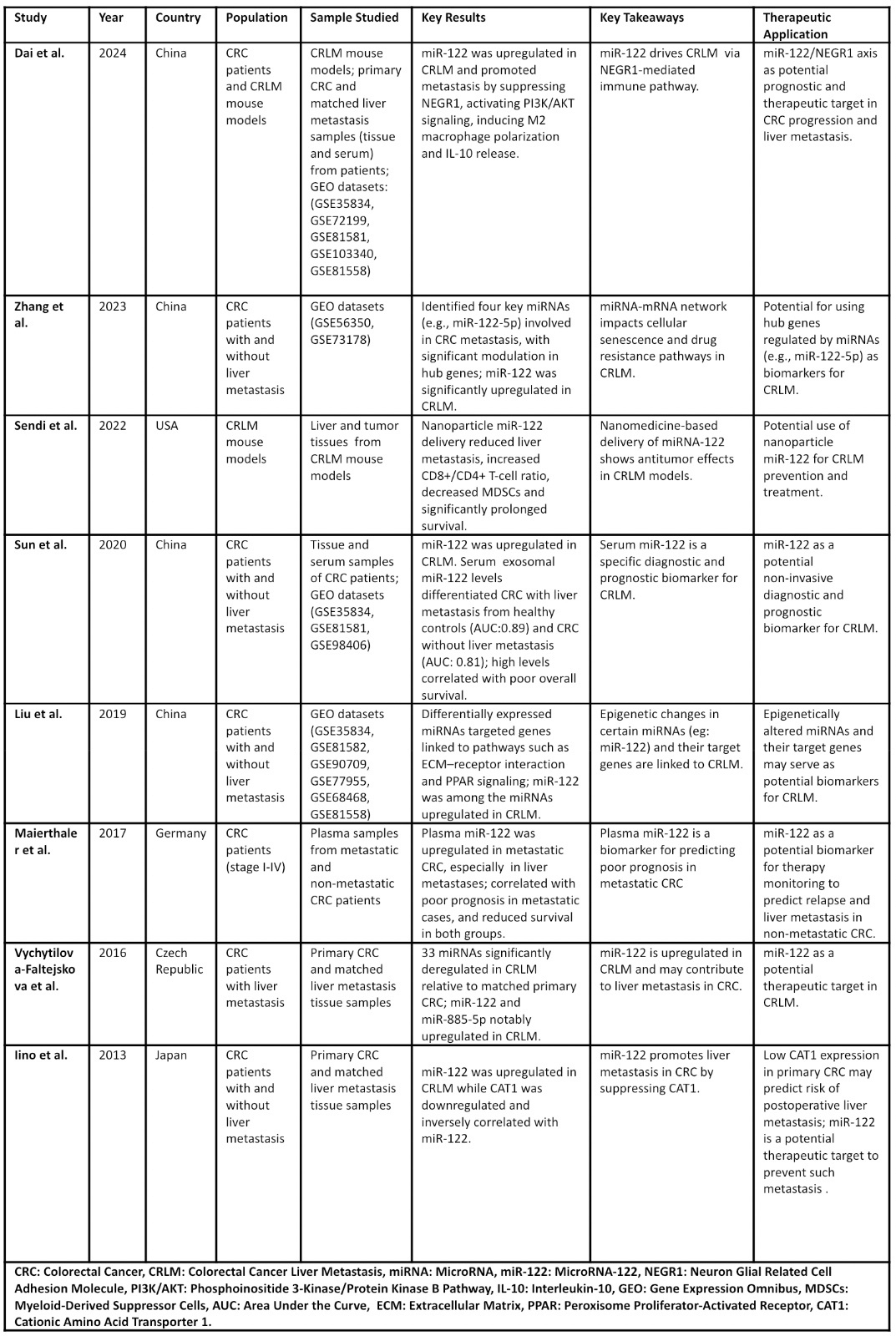
Results:
The inclusion criteria were met by eight studies, each highlighting the unique role of miR-122 in CRLM. This review found consistent upregulation of miR-122 in liver metastases, with individual studies linking it to metastatic progression via targets such as CAT1, NEGR1, and inflammation-related pathways. In CRC mouse models, miR-122 delivery via nanoparticles was shown to reduce liver metastasis, and enhance immune responses in hepatic tissue, suggesting therapeutic potential. Serum exosomal miR-122 was identified as a promising non-invasive biomarker, with potential utility in early diagnosis and prognosis of CRLM. Additionally, epigenetic alterations of miRNAs (including miR-122) and their target genes were observed to contribute to CRC liver metastasis through dysregulation of metastasis-associated signaling pathways.
Discussion:
The regulation of CRLM is significantly influenced by microRNAs, particularly miR-122, which presents valuable opportunities for the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic methods. There is a potential to improve the clinical outcomes of CRC patients with liver metastases by prioritizing clinical trials that evaluate miRNA-based treatments and assessing serum miRNAs as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers in future research.
Disclosures:
Diksha Sanjana Pasnoor, MBBS1, Rishabh Vashisht, MBBS2, Arshad Ali Mohd, MBBS3, Lakshmi Sai Meghana Kodali, MBBS, MPH4, Naga Sai Akhil Reddy Gogula, MBBS5, Swathi Nimmala, MD6, Rineetha Tandra, MD, MBBS7, Sudhir Pasham, MD8, Sandeep Kotnani, MBBS9, Devangi Upadhyay, MBBS10, Rupak Desai, MBBS11. P0295 - The Role of miR-122 in Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis: A Systematic Review of Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Potential, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
